Asia Impact Investment Report
World Economic Forum (WEF) releases Asia Impact Investment Report, which aims to summarize the development of the Asian impact investment market and provide recommendations.
World Economic Forum believes that the Asian impact investment market is still in its early stages, and impact investments based on climate and nature solutions have great growth potential.
Related Post: Global Impact Investing Network Releases 2024 Impact Investment Market Report
Background of Asian Impact Investment
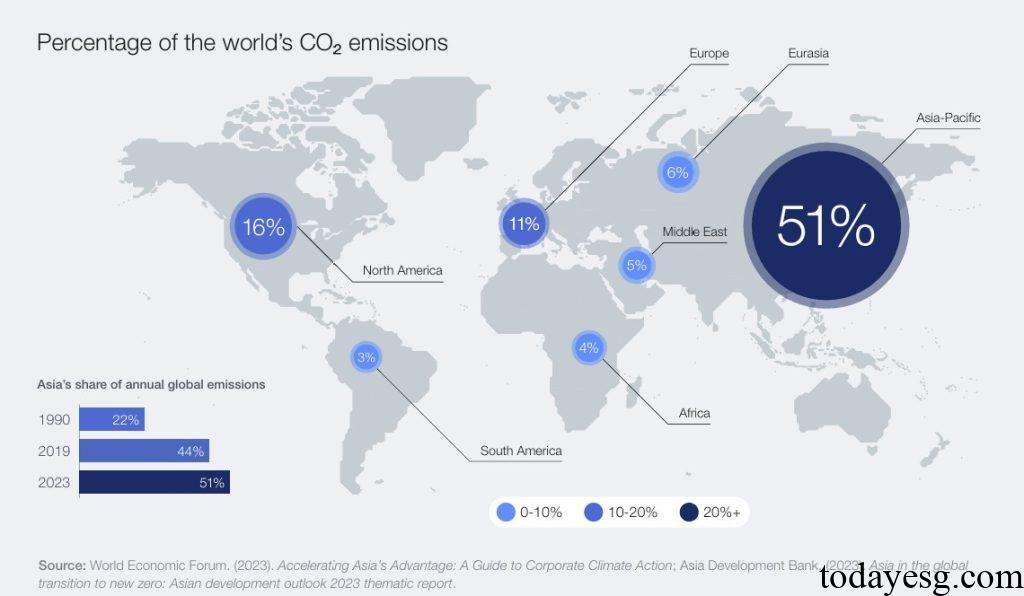
Asia is the region with the highest carbon emissions in the world, accounting for 51% of the global total, more than doubling from 1990 (22%). Asia is also the most populous region in the world, with a total population of 4.68 billion. Asia is greatly affected by climate change, with 30% of its economic growth coming from natural resources. If measures are not taken to address climate issues, by 2070, 6 to 12 million people in Asia will leave their original homes due to climate change.
Impact investing is an important way to address carbon emissions and climate change issues in Asia, as it can generate positive and measurable social and environmental impacts while generating financial returns. In recent years, many international investors have been conducting impact investing in Asia, achieving both portfolio diversification and their investment goals.
Asian Impact Investment Challenge
Despite receiving widespread attention as an emerging region for impact investing, there are still some factors in Asia that have an impact on investment. The World Economic Forum conducted a survey of impact investment experts, and many respondents believe that the Asian impact investment market is still in its early stages, with many financial policies (such as investment taxonomies) being incomplete. This is not only a regional issue, but also a problem faced by the entire impact investment industry. Institutional investors are more inclined to invest in mature investment projects such as renewable energy, as these projects typically have clear regulatory frameworks and investment pathways.
Some experts believe that impact investing in Asia lacks a mechanism for measuring its impact, as it may have unique risk return calculation methods and investors have limited access to data. Some climate investments may have a term of more than fifteen years, making it difficult for investors to track the long-term impact of their investments. In addition, many Asian regions face significant investment management challenges due to their small geographical size and distant location, making it difficult to obtain critical investments.
Asian Impact Investment Recommendations
The World Economic Forum believes that the development of the Asian impact investment market can be considered from the following aspects:
- Blended financing: Some impact investment projects have immature business models, and blended financing is the key to solving this problem. This approach can provide investors with diversified choices and reduce investment risks.
- Collaboration opportunities: Stakeholders can collaborate on investments to diversify risks. Some public financial institutions can provide preferential capital or charitable capital to take on higher financial risks and attract private investors.
- Coordinated action: Different stakeholders have different investment preferences and impact on investment goals. Therefore, choosing suitable partners and coordinating overall actions can promote impact investment and meet the requirements of all aspects.
- Investment standards and taxonomies: Consistent impact investment standards and taxonomies can compare different projects and improve data quality and quantity. Some Asian jurisdictions have begun to establish taxonomies to provide guidance for influential activities for investors.
Reference:
Accelerating Impact Investments for Climate and Nature in Asia








