Guidance for Investing for Sustainability Impact
The United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment (UNPRI) releases guidance for investing for sustainability impact (IFSI), aimed at providing a framework for investors to implement investing for sustainability impact and offering solutions to potential problems.
The United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment believes that sustainability is an important factor that long-term investors must pay attention to, and ignoring this factor may lead to investors being unable to fulfill their fiduciary responsibilities. Investing for sustainability impact is an important approach to addressing this issue.
Related Post: Introduction to Sustainable Investment Classification Method Released by Eurosif
Background of Investing for Sustainability Impact
Investing for sustainability impact has become an important consideration for regulatory agencies when formulating policies. In March 2018, the EU identified achieving sustainable and inclusive growth as a key goal in its Sustainable Finance Action Plan. In October 2022, the UK Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) stated in the Sustainability Disclosure Rules that consumers must be able to trust sustainable investment products that can have a positive impact on the environment and society.
Investing for sustainability impact typically focuses on addressing systemic risks. Climate change is an important representative of systemic risk, which can lead to financial risks and affect investors’ financial goals. Asset owners and asset managers may reduce carbon emissions through IFSI in order to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Investing for sustainability impact is different from impact investing, as impact investing aims to generate positive, measurable social and environmental impacts and achieve financial returns. Investing for sustainability impact is a broader investment approach that focuses on a range of actions that investors can take, such as asset allocation, stewardship, and policy engagement. Sustainable impact investing applies to the entire investment process and to all asset classes to help investors pursue sustainable development outcomes.
Framework for Investing for Sustainability Impact
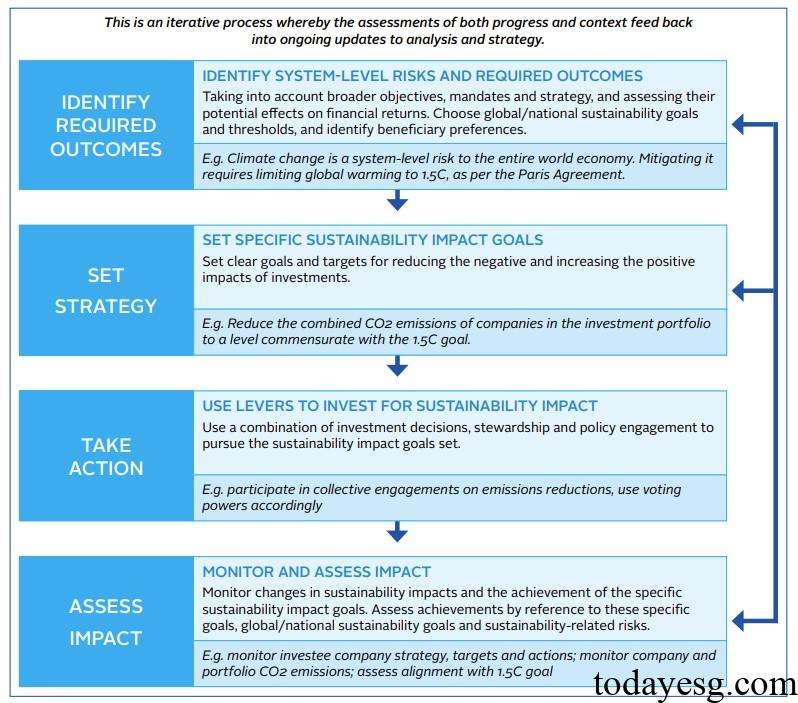
In order to assist signatories in implementing sustainable investment, the United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment have developed a framework for investing for sustainability impact, which includes the following contents:
- Determine intention: Investors need to determine their purpose, such as their beliefs, financial return goals, and the relationship between these beliefs and sustainable impact. Investors need to consider systemic risks and opportunities related to financial goals and disclose their goals and associated systemic risks and opportunities. Common practices include reducing the cost of negative environmental impacts, addressing non-diversifiable portfolio risks, and responding to regulatory pressures on sustainability issues.
- Set goal: After determining the goal, investors need to set one or more sustainable development goals that support the goal, preferably with timeliness and specificity. Common practices include reducing greenhouse gas emissions with the goal of achieving net zero emissions by the specified date.
- Take action: After setting goals, investors need to take action to achieve them. For example, through strategic asset allocation to achieve sustainable development goals, selecting different investment managers, actively managing invested companies, and eliminating investments that conflict with sustainable development goals.
- Measure progress: Investors need to demonstrate to stakeholders the results of implementing sustainable impact investments, describing their efforts and progress. Investors need to determine whether their actions have the expected impact on sustainable goals or on their financial objectives.
The UNPRI believes that there are some challenges to investing for sustainability impact. Changes in regulations and policies may make it difficult for investors to determine long-term sustainable development goals, and some areas that lacks infrastructure may hinder sustainable investment, which may be the easiest places for sustainable impacts to make a difference. The additional research and due diligence costs incurred to achieve sustainable impact investments may impose a budget burden on asset owners. The IFSI framework will continue to be updated to address these practical issues.
Reference:
Investing for Sustainability Impact Report: Guidance Informed by the Legal Framework for Impact








