Banking and Green Building Report
The United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI) releases a report on banking and green buildings, aiming to explore how the banking industry can support the development of green buildings.
UNEP FI believes that the carbon emissions of the construction industry account for 37% of the total global greenhouse gas emissions, and carbon reduction in the construction industry has high cost-effectiveness and impact. Members of the Principles for Responsible Banking should actively pay attention to the development of green buildings.
Related Post: UNEP FI Releases Climate Target Setting Checklist for Banking Industry
Development and Impact of Green Building Industry
The development of the green building industry is closely related to the Principles for Responsible Banking, and all six principles corresponding, such as:
- Principle 1 Alignment: Banks should align their operations with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) and the Paris Agreement. Green buildings can help achieve multiple United Nations Sustainable Development Goals such as clean energy, sustainable cities, responsible production, and climate action.
- Principle 2 Impact and target setting: Banks should set a net zero target to reduce negative impacts on society and the environment while increasing positive impacts. Green buildings have measurable data on water resources, energy, and carbon emissions, providing feasible operations for banks to set business goals.
- Principle 3 Clients and customers: Banks should collaborate with clients to support them in achieving sustainable development goals. Banks can provide sustainable financial products and technical assistance for green buildings and invest in green real estate portfolios.
- Principle 4 Stakeholder engagement: Banks should develop responsible strategies with stakeholders. Banks can participate in green building activities and influence their development.
- Principle 5 Governance and culture: Banks should integrate responsible business into a culture of governance. Banks can provide green building related training for employees and develop relevant incentive measures.
- Principle 6 Transparency and accountability: Banks should publicly disclose their net zero commitments and progress and take responsibility for their actions. Banks can participate in green building certification programs to measure and disclose the emission reduction effects of green buildings.
Relationship between Banking and Green Building
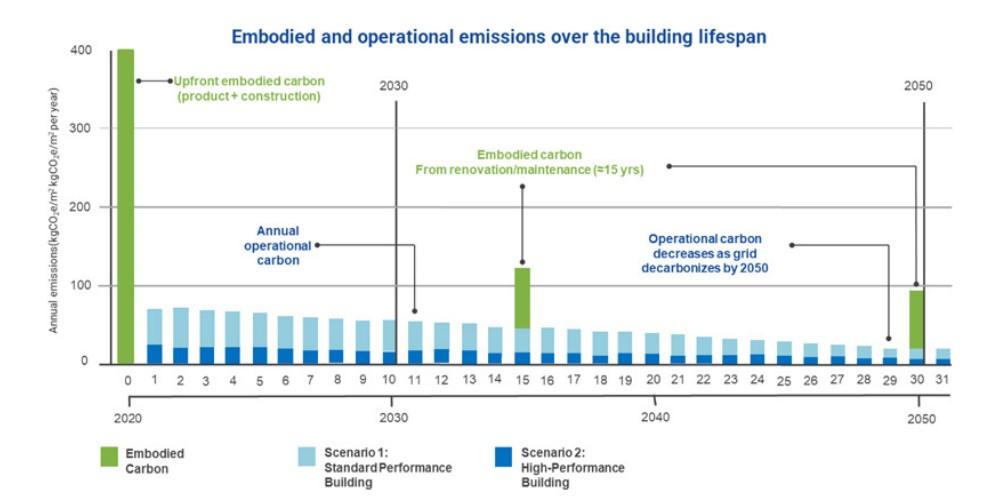
To set clear, quantifiable, and verifiable goals for the green building industry, the banking industry needs to understand the relevant environmental indicators of the construction industry and link their business objectives to them. Firstly, there are two types of carbon emissions in the construction industry, namely operational emissions and embodied emissions. Operational emissions refer to the greenhouse gas emissions generated during the operation of buildings due to heating, cooling, lighting, and ventilation functions. Embodied emissions refer to greenhouse gas emissions generated during the extraction, production, transportation, disposal, and construction processes of building materials.
According to the Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction, operational emissions account for 73% of total emissions and embodied emissions account for 27% of total emissions. In addition to classification, another important indicator for measuring carbon is Whole Building Life Cycle Assessment, which quantifies the carbon emissions of buildings from construction, operation, maintenance to final destruction and disposal. As the cycle progresses, operational emissions gradually decrease, and embodied emissions will also experience a phased decline.
How to Support Green Building in Banking Industry
The United Nations Environment Programme Financial Initiative believes that the banking industry can reduce operational and embodied emissions from buildings in the following directions:
- Design a green building asset strategy: The banking industry can develop a strategic roadmap for green buildings and measure the impact of building portfolios. There are already various ESG tools available worldwide, such as the Global Real Estate Sustainability Benchmark. Banks need to set emission reduction targets based on science and choose green certification to measure the carbon emissions of building combinations.
- Develop sustainable financing and green building products: Banks can incorporate green buildings into their financial products such as loans, insurance, bonds, stocks, etc., and can also provide mixed financing solutions with public financial institutions. Banks can also hire third-party consultants to provide technical support for green building related clients.
- Promote internal innovation in banks: Banks can provide training and other incentives for employees to participate in green building business, understand sustainable financial products related to green buildings, and communicate with customers.
- Impact the lifecycle of the construction industry: Banks can collaborate with regulatory agencies and other stakeholders to provide green building consulting, and participate in the formulation of carbon reduction policies, thereby changing the emissions of the construction industry.
Reference:








