Discussion Paper on Nature Transition Plan
The Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) releases a discussion paper on nature transition plans, aimed at providing guidance for businesses and financial institutions to develop and disclose nature transition plans.
The TNFD believes that nature transition plan is an important approach to achieving the Global Biodiversity Framework and it is a key focus for stakeholders. Some organizations that have already developed climate transition plans are developing natural transition plans to achieve comprehensive planning.
Related Post: TNFD Issues Recommendations on Nature-related Information Disclosure
Introduction to the Nature Transition Plan
The TNFD believes that a nature transition plan refers to a part of an organization’s overall business strategy, which is based on the organization’s goals, actions, accountability mechanisms, and expected resources, responding to and promoting the transition proposed by the global biodiversity framework, in order to reverse biodiversity loss by 2030 and achieve natural restoration by 2050. The TNFD provides steps for identifying and evaluating nature related dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities based on the LEAP method:
- Locate: Find the place where the organization interacts with nature.
- Evaluate: Evaluate an organization’s dependence and impact on nature.
- Assessment: Measure nature related risks and opportunities.
- Prepare: Prepare to respond to and report on substantive natural matters.
The TNFD believes that organizations can use the LEAP approach to first identify natural priorities and develop nature transition plans based on them, and expand coverage and accuracy over time. The Transition Pathway Taskforce believes that natural transition programs need to have effective goals, specific action steps, and strong disclosure mechanisms to improve their efficiency.
Contents of the Nature Transition Plan
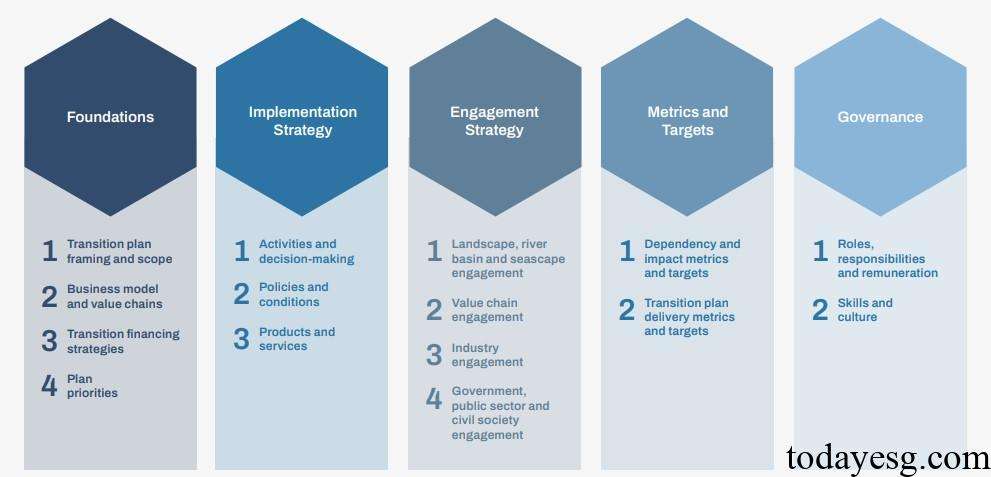
The TNFD refers to the document of the Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero (GFANZ) and divides the nature transition plan into five parts, namely Foundations, Implementation Strategy, Engagement Strategy, Metrics and Targets, and Governance. The contents of each section are as follows:
- Foundation: The basis for an organization to develop a nature transition plan, including the scope of the transition plan, business model, transition financing strategy, and plan priorities.
- Implementation strategy: A series of actions developed by the organization for each plan priority, including action plans to achieve the priority, policy conditions developed to support the transition plan, and the impact of the transition plan on products and services.
- Engagement strategy: How the organization collaborates with other stakeholders to implement transition plans, including participation from regions, value chains, suppliers, industry partners, and public sector.
- Metrics and Targets: Indicators for monitoring the progress of the organizational transition plan, including indicators related to natural dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities, as well as indicators used to monitor the implementation progress and performance of the transition plan.
- Governance: The governance outcomes established by an organization to achieve natural transition goals, including roles and responsibilities defined for the transition plan, as well as relevant skills and culture.
How to Disclose Nature Transition Plan
The TNFD recommends that organizations disclose any implemented transition plans and how these plans align with the global biodiversity framework. IFRS S1 requires organizations to disclose information on risks and opportunities related to sustainable development. Some regional standards, such as the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), also recommend that organizations disclose their biodiversity transition plans. The TNFD, based on the 19 disclosures released by the Transition Path Taskforce, sets the following disclosure elements:
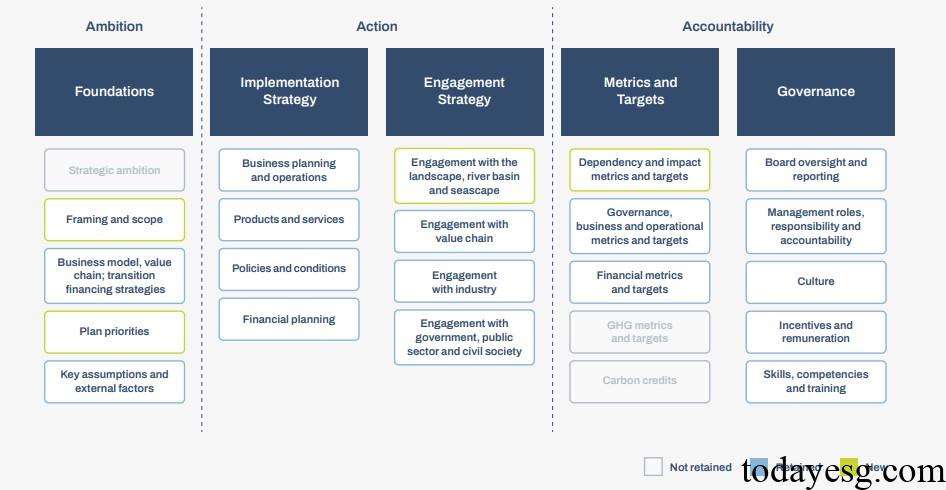
The TNFD divides the above five themes into three parts, namely Ambition, Action, and Accountability. New disclosure elements have been added below each theme, and some inappropriate elements have been removed. Companies can complete disclosures based on these elements, making it easier for stakeholders to monitor the progress.
Reference:








