Reduce Transition Risk of Investment Portfolio
Investors have noticed the risks and opportunities brought by climate change and hope to reduce the transition risk of their investment portfolio. This article introduces the Low Carbon Transition Rating released by Sustainalytics, which can measure the transition risks of companies and funds and assist asset managers and owners in their decision-making.
Sustainalytics measures the transition risk of 10000 companies and 60000 funds worldwide in its report, helping investors identify companies and financial products in different industries and regions that are more in line with low carbon transition goals.
Related Post: MSCI Releases Global Carbon Credit Project Ratings Report
Low Carbon Transition Rating for Companies
The low carbon transition rating is a forward-looking indicator based on science, which can evaluate whether a company meets the net zero emission path. The low carbon transition rating of companies is measured by the Implied Temperature Rise, which represents the distance of the company from the 1.5 degree Celsius warming path. Sustainalytics evaluates carbon reduction plans, policies, and programs for low carbon transition of companies, in order to calculate implicit warming indicators, and assigning the results to one of five ratings.
Sustainalytics finds that currently no company conforms to the 1.5 degree Celsius warming path, and 17% of companies conform to the 1.5-2 degree Celsius warming path. Most companies are located on the warming path of 2 to 3 degrees Celsius (73%), and these companies are likely to gradually meet the goals of the Paris Agreement in future actions. From a geographical analysis, the rating performance of developed economies is generally lower than that of developing economies, which may be due to developed economies taking on more tasks in the decarbonization path, while developing economies have gained more time in the decarbonization path.
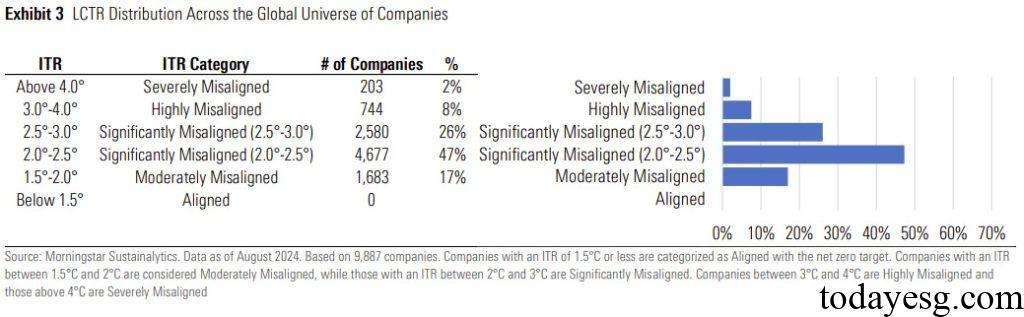
Low Carbon Transition Rating for Funds
Sustainalytics calculates the warming path of investees in the fund to obtain a low carbon transition rating for the fund, where funds with lower implied warming are more in line with the net zero path. The data shows that the performance of the low carbon transition rating of funds is lower than that of companies, with only 2.3% of funds meeting the heating path of 1.5 to 2 degrees Celsius, while the proportion of companies meeting this heating path is 17%. 90% of funds are located on a warming path of 2 to 3 degrees Celsius. The poor performance of fund ratings may be due to the fact that most funds tend to allocate assets to companies in developed economies.
From a geographical perspective, the low carbon transition rating of developed market funds is also underperformed. The Implied Temperature Rise in Canada and the United States is 2.8 degrees Celsius and 2.7 degrees Celsius, respectively, while the average implied warming in developing economies is 2.4 degrees Celsius.
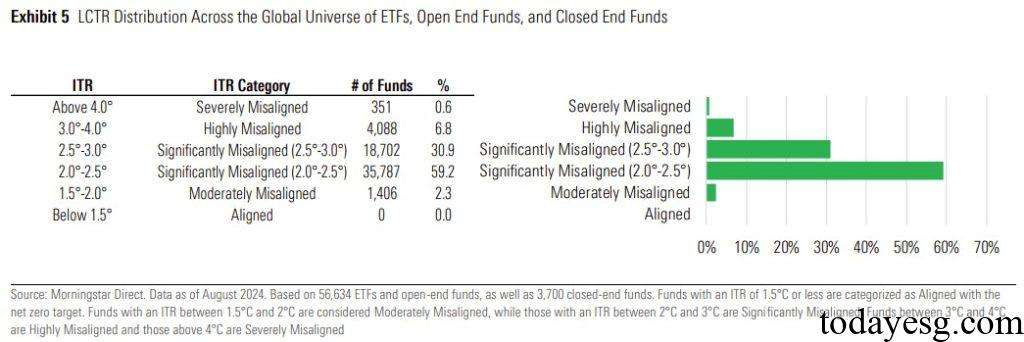
Application of Low Carbon Transition Rating
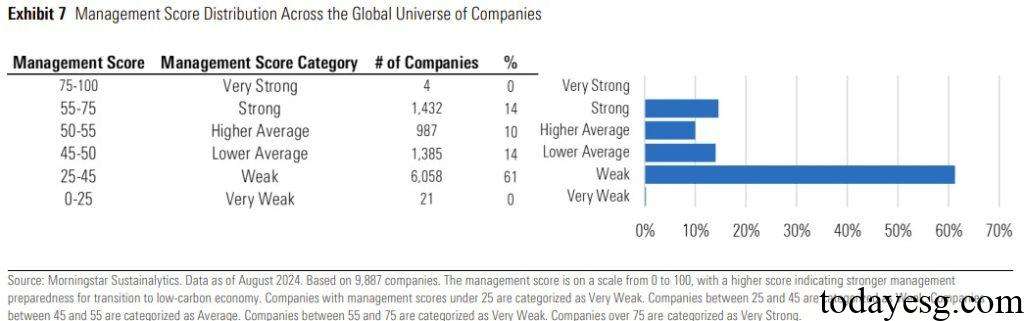
In addition to Implied Temperature Rise, low carbon transition rating also provides some indicators that investors can refer to. For example, the Management Score, which measures a company’s ability to manage low carbon transition risks through 85 indicators. Data shows that over 24% of global companies have a management score greater than 50, indicating that these companies may reduce their baseline carbon emissions in future actions.
Low Carbon Transition Value at Risk (LCT VaR) is another indicator that represents the potential losses that a company may incur during its low carbon transition. It is based on the impact of future carbon pricing on the company’s emissions and indicates the impact of transition risk on the company’s future value. The data shows that the energy industry (24.4%), natural resources industry (18.6%), and utilities industry (8.8%) have the highest LCT VaR. Developing economies have lower LCT VaR and may benefit from lower carbon prices.
Reference:
Measuring Transition Risk and Climate Action in Portfolios Report





