Global Carbon Credit Project Ratings Report
MSCI releases a global carbon credit project ratings report, aimed at analyzing the integrity of global carbon credit projects through the MSCI Carbon Project Ratings.
MSCI believes that the quality of carbon credits is a key factor in carbon projects. The Taskforce for Scaling the Voluntary Carbon Market finds that 45% of buyers consider integrity as a core issue in the market. According to a survey by the Science Based Targets Initiative, 55% of respondents are concerned that using carbon credits with insufficient integrity may result in greenwashing risks.
Related Post: CDP Releases Position Paper on Carbon Credits
Measurement of Carbon Credit Integrity
The differences in project types, quantification methods, and potential benefits of carbon credit projects have led to a lack of a consistent measurement method. In recent years, the market has been implementing multiple measures to address integrity. There are currently over 50 carbon credit registries worldwide, which develop methods and maintain infrastructure for tracking carbon credit issuance and cancellation. Most carbon credit registries are small in scale and typically operate within jurisdictions. Some large registries, such as Verra and Gold Standard, have already covered hundreds of carbon credit projects.
In addition to registries, some carbon credit integrity initiatives and frameworks are also expanding their influence. The Integrity Council for the Voluntary Carbon Market (ICVCM) was established in 2021 with the aim of improving the integrity standards of the carbon credit market. In 2023, the committee launched measurement standards that include governance, emission impact, and sustainable development, and announced the first batch of carbon credit projects that meet the standards in 2024. Other common initiatives include the Carbon Credit Quality Initiative and the Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation.
Carbon credit insurance and carbon rating are the two latest directions for market development. Carbon credit insurance products focus on measuring the delivery risk and reversal risk of carbon credits, but are still in the early testing stage. Carbon rating products provide investors and buyers with a guarantee of the integrity by conducting in-depth evaluations of the projects.
Introduction to MSCI Carbon Credit Project Rating
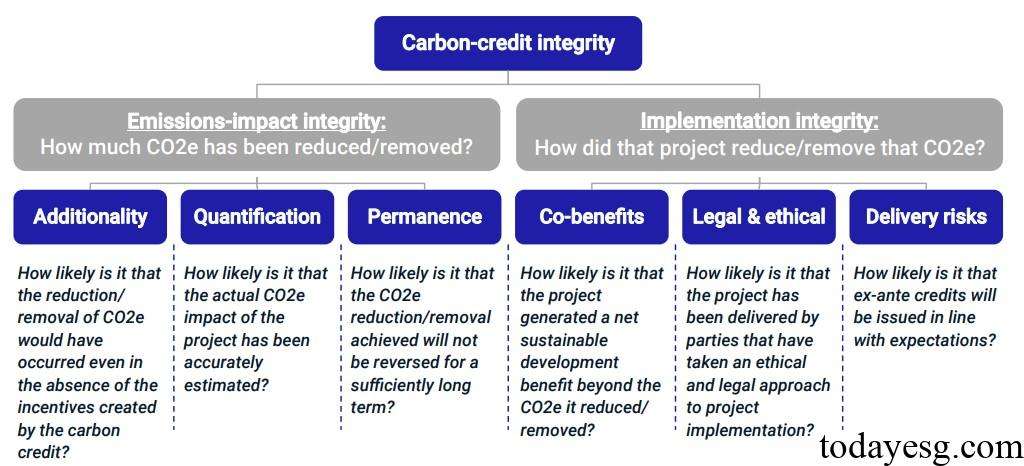
The MSCI Carbon Credit Project Rating independently evaluates the integrity of carbon credit projects based on multiple criteria. The rating comes from the 2021 carbon credit integrity assessment system and is based on the measurement standards of the ICVCM. Each project is evaluated based on six criteria and over fifty sub criteria. Carbon credit integrity is divided into two categories: emissions impact integrity and implementation integrity, each of which contains three criteria, namely:
Emissions Impact Integrity:
- Additionality: The degree to which carbon emission projects are affected by the funds obtained from selling carbon credits. If a carbon reduction activity continues to develop without selling carbon credits, then selling carbon credits will not result in additional carbon reductions.
- Quantification: Assuming the baseline scenario of the project is accurate, the likelihood that its carbon emission impact can be correctly assessed. MSCI uses multiple benchmarks and methods to evaluate the accuracy of projects and reduce the probability of overestimating carbon emissions.
- Durability: Degree of permanent removal or reduction of carbon emissions, applicable to carbon storage and capture projects, except for projects that can reduce carbon emissions without storage.
Implementing Integrity:
- Co-benefits: The environmental and social impacts that carbon projects may generate. The co-benefits assessment adopts the framework of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
- Legal & Ethical: Whether the project involves legal and ethical risks, and whether the purchasing these projects affect the buyer’s reputation.
- Delivery Risks: Whether the project can achieve its carbon credit targets as expected, which may come from financial, operational, and registration risks of the project.
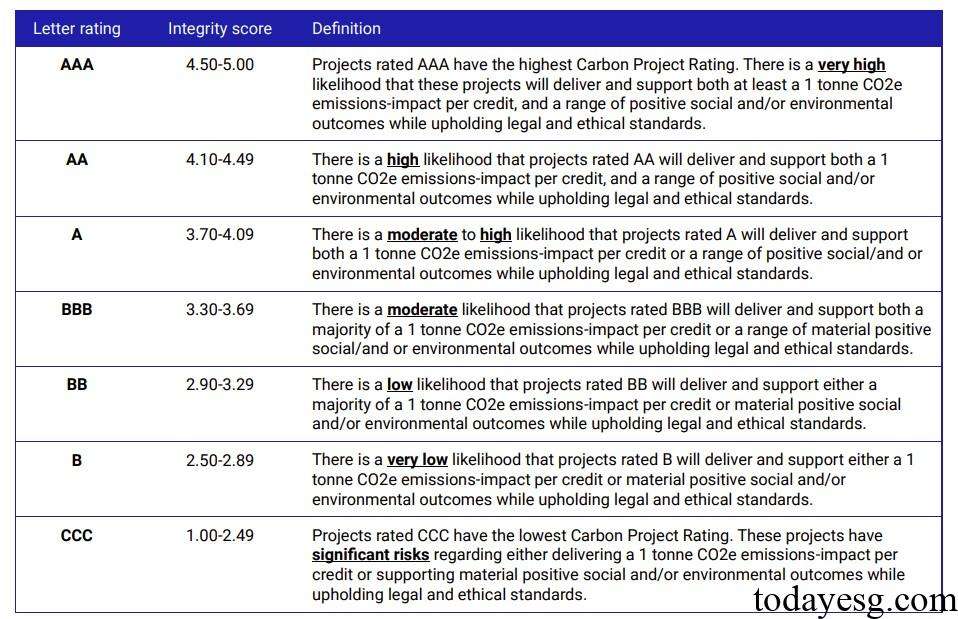
MSCI evaluates each criteria and sub criteria on a scale of 1 to 5, where 1 indicates a low level of integrity and 5 indicates a high level of integrity. These standards are used to calculate the overall integrity score of carbon projects through reverse weighting. The reverse weighting method assigns higher weights to standards with lower scores, and the overall score will be converted into a letter rating. Due to the different preferences of stakeholders for standards, users of the MSCI carbon market platform can set their own weights for calculation.
Integrity Analysis of Global Carbon Credit Projects
MSCI analyzes over 4000 carbon credit projects using the carbon project rating method and obtained the following insights:
- Low integrity projects are prevalent, but overall they are improving: MSCI finds that low integrity projects (rated B or below) issued in the first half of 2024 accounted for 39% of the total. So far, 55% of the released projects and 59% of the withdrawn projects are low integrity projects. Currently, no project has received the highest AAA rating, but since the first half of 2022, the proportion of CCC rated projects in the market has decreased by 10%, while projects with A ratings or above have increased by 5%, indicating that the overall project rating is improving.
- The co-benefits and risks within the same project type vary greatly: Heterogeneity of different projects has an impact on the co-benefits and risks of the projects. For example, renewable energy projects are all related to United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 7 (affordable clean energy), but due to the technical characteristics of different projects, different categories of sustainable development goals may be involved. In addition, the design and implementation methods of the project also lead to differences in their co-benefits and risks.
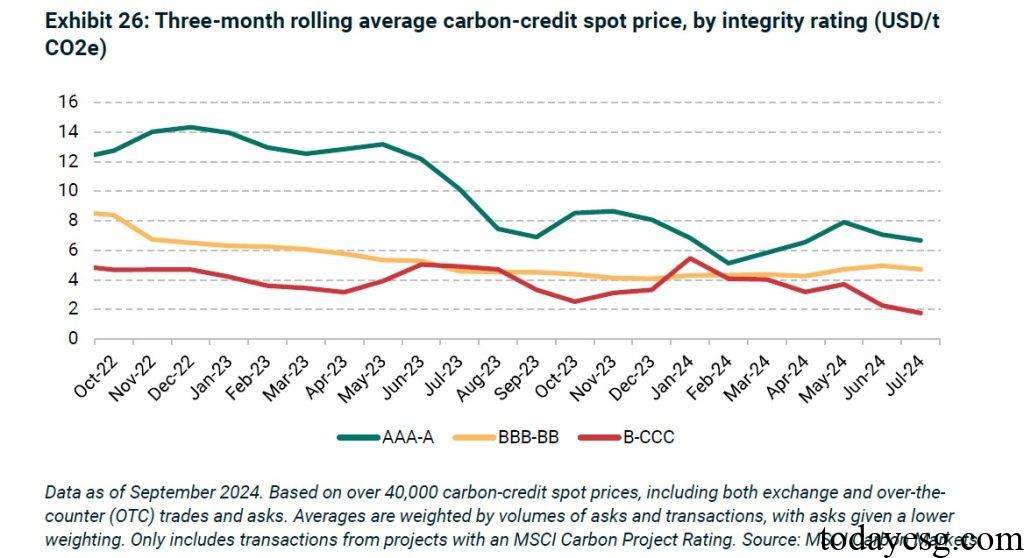
- Integrity is the driving factor of carbon credit prices: MSCI draws a trend chart of carbon credit prices based on different levels of integrity, and finds that for every 1 increase in integrity score, carbon credit prices will rise by 8%. In terms of specific standards, the criteria of co-benefit, law, and ethics will have a positive impact on carbon credit prices, while durability will have a negative impact on carbon credit prices. Additionality and quantification is not statistically significant.
Reference:








