2024 ESG Asset Owner ESG Survey Report
Morningstar releases 2024 Asset Owner ESG Survey report, aimed at understanding the opinions of global asset owners on ESG investment methods, strategies, data, and ratings.
Asset owners are essential participants in the financial market and also play a crucial role in ESG investments. The opinions of asset owners can influence the development of the ESG market, and therefore deserve special attention.
Related Post: Morningstar Releases 2023 Asset Owner ESG Survey Report
Asset Owners’ ESG Investment Allocation
Morningstar collects the opinions of 500 asset owners in a survey, including outsourced chief investment officers (20%), pension funds (19%), insurance companies (19%), and family offices (17%), with a cumulative asset management scale of $18 trillion. All respondents invest a portion of their funds in ESG assets. In 2022, 29% of respondents invested more than half of their funds in ESG assets, and this proportion increases to 35% in 2024. In terms of the proportion of ESG assets, Europe (45%), Asia (41%), and the Americas (37%) rank high.
In terms of ESG asset categories, listed company stocks (36%), private equity and private debt (25%), real estate (24%), and bonds (14%) are the most common categories by respondents. In terms of reasons for allocating ESG assets, senior management requirements (36%), regulatory requirements (30%), and stakeholder pressure (29%) rank high. In terms of obstacles faced in ESG investments, return impact (44%), lack of standardized data (39%), and stakeholder attitudes (34%) rank high. Asset owners rely on a similar ratio of internal and external resources when implementing ESG investments, with 22% of asset owners establishing dedicated ESG investment teams.
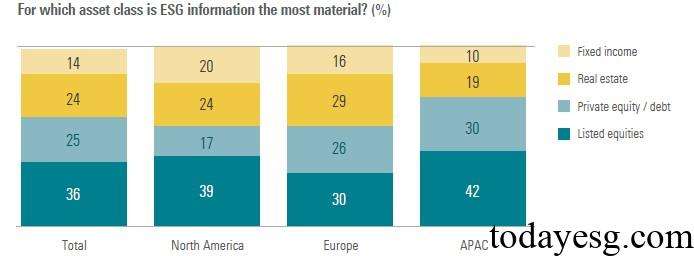
Asset Owners’ Judgment of ESG Factors
More than two-thirds of asset owners believe that ESG has become more important in the past five years, with Asia (71%), Europe (68%), and the Americas (61%). In terms of specific factors, 64% believe that environmental factors are more important (compared to 52% last year), 58% believe that social factors are more important (compared to 38% last year), and 55% believe that governance factors are more important (compared to 43% last year).
In terms of environmental factors, net zero emissions (55%), energy management (49%), and water resource management (33%) are the key concerns. In terms of social factors, labor force (51%), community relations (42%), and customer privacy (41%) are the key concerns. In terms of governance factors, business ethics (54%), risk management (43%), and regulatory environment (40%) are the key concerns. 72% of asset managers agree with the relationship between single materiality and ESG factors, while 59% of asset owners agree with the relationship between double materiality and ESG factors. 53% of asset owners believe that ESG is closely related to fiduciary responsibility, with Asia (57%) having the highest percentage.
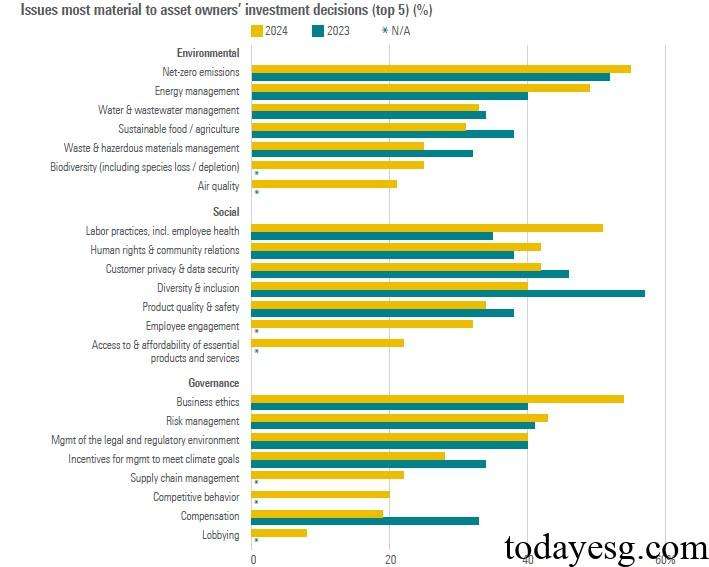
External ESG Factors Affecting Asset Owners
In terms of the impact of regulatory policies on ESG investments, 53% of respondents believe that regulatory policies have had a positive effect, an increase of five percentage points compared to last year. These positive impacts include improving company information disclosure (54%), providing clear definitions (53%), and developing standardized frameworks (53%). 26% of respondents believe that regulatory policies pose obstacles to ESG investments, with the main issue being the burden of information disclosure (53%), an increase of 29 percentage points compared to last year.
In terms of the impact of ESG data, ratings, and indices on ESG investments, 43% of respondents believe that ESG data is the most important factor in implementing ESG investments, surpassing those who choose ESG ratings (24%) and ESG indices (23%). More than half of the respondents state that ESG data, ratings, and indices have improved in the past five years, and the market still expects to continue improving the accuracy and standardization of data. Asset owners consider rating agencies (36%), regulatory agencies (33%), and international institutions (32%) as important participants in improving ESG data, ratings, and indices.
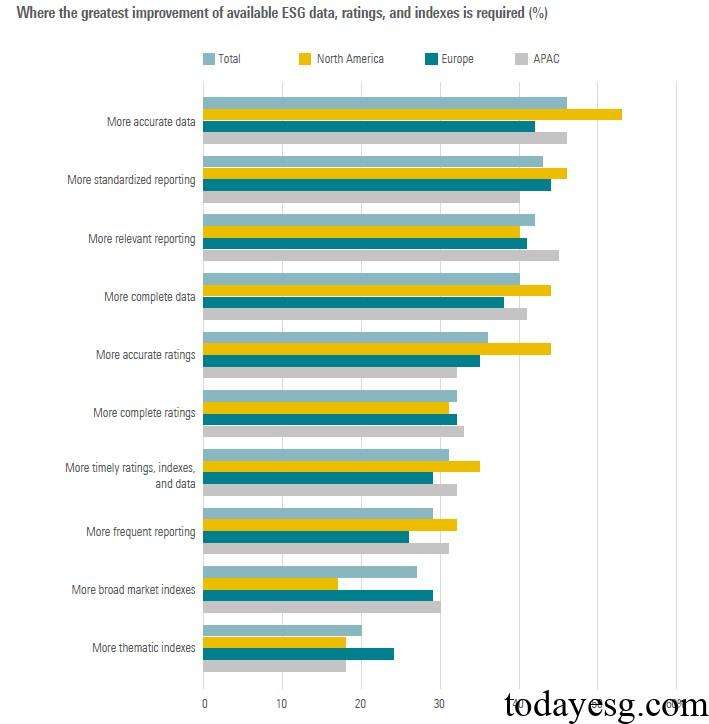
Reference:








