Global Green Talent Supply and Demand Report
LinkedIn releases a report on global green talent supply and demand, aiming to analyze the trends in green talent in recent years, and predict the future developments.
LinkedIn summarizes 600 green skills in 12 categories based on taxonomy, divides them into three different green categories based on occupational characteristics, and combines the information in the database to obtain the supply and demand trends of green talents.
Related Post: PwC Releases Green Talents and Skills Report for Financial Industry
Global Green Talent Demand Changes
LinkedIn categorizes green skills into 12 types, including pollution prevention, waste prevention, energy management, renewable energy generation, environmental remediation, ecosystem management, sustainable education, sustainable research, environmental auditing, environmental policy, sustainable procurement, and environmental finance. These categories involve a total of 600 green skills, and their data comes from information listed by LinkedIn users or information obtained from their research fields, titles, and job advertisements.
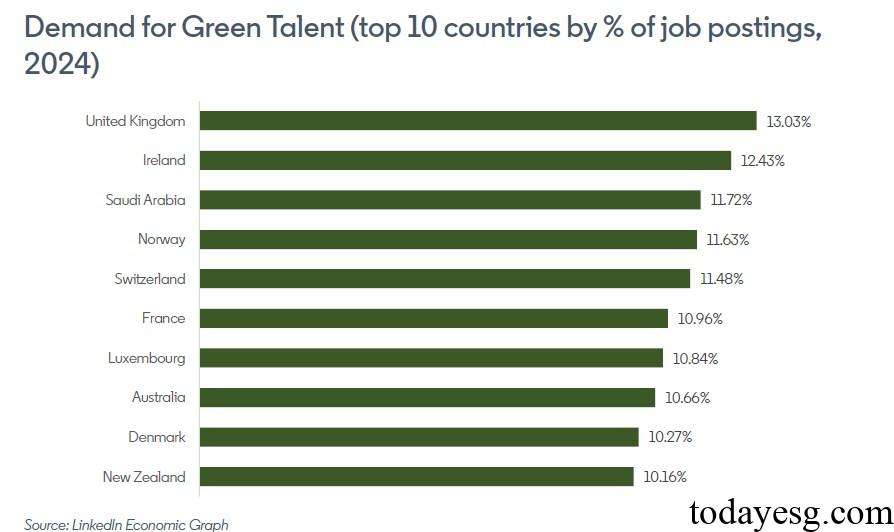
The average annual growth rate of global green talent demand from 2021 to 2024 is 5.4%. In 2021, 6.8% of job postings on LinkedIn involved green jobs or required green skills, and by 2024, this proportion has increased to 7.5%. As of July 2024, the UK has the highest percentage of demand for green talent, with 13% of job postings related to green talents.
Among the 43 countries surveyed by LinkedIn, the demand for green talent in 28 countries increases year-on-year, while the demand for green talent in 15 countries decreases year-on-year. But according to the data from 2021, the demand for green talents has increased in most countries.
Global Green Talent Supply Changes
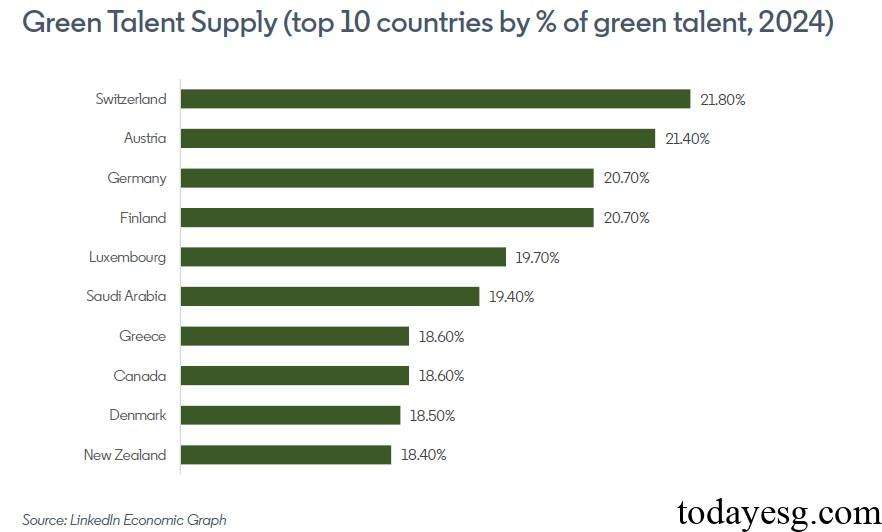
The average annual growth rate of global green talent supply from 2021 to 2024 is 3.2%, which is lower than the growth rate of demand. In the past year, the growth rate of green talent supply was 5.6%, with Switzerland (21.80%), Austria (21.40%), Germany (20.70%), and Finland (20.70%) having relatively high percentages of green talent.
Among the 43 countries surveyed by LinkedIn, the supply of green talent is increasing in all countries, but the median growth rate (5.6%) is only half of the median growth rate of green talent demand (11.6%). From 2021 to 2024, there are green talent gaps in 28 countries. Therefore, when investing globally in green transition, this phenomenon also needs to be considered.
The imbalance between supply and demand of green talents has led to a significantly higher recruitment rate for green talents than the overall recruitment rate. For example, in the United States, the recruitment rate for green talent has been 80.3% higher than the overall recruitment rate in the past year, while in the United Kingdom, this number comes to 72%. Despite a decline in demand for green talent in some countries, their recruitment rates for green talent remain above average.
Future Development of Green Talent Market
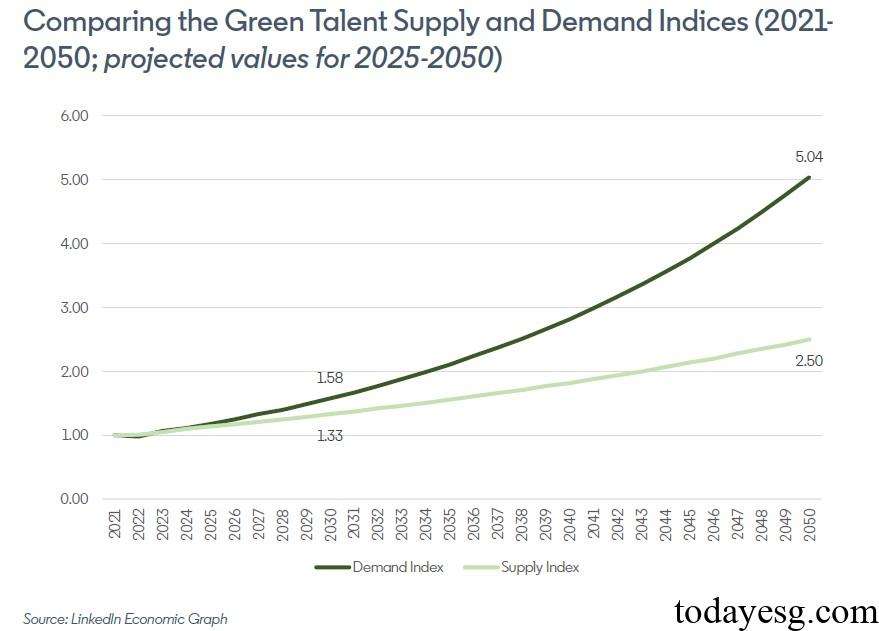
LinkedIn compares the changes in the Green Talent Demand Index and Supply Index based on data from 2021 to the present. As of 2024, the Demand Index is 1.2% higher than the Supply Index. If the current growth rate is maintained, this difference will reach 18.7% in 2030 and 101.5% in 2050. In order to meet market demand, the green talent supply needs to double by 2050. With the gradual improvement of the green skills taxonomy, the demand and supply will continue to change.
By 2025, each jurisdiction will submit a Nationally Determined Contributions report and set a net zero target for 2030. LinkedIn expects the report to involve plans to actively cultivate green talents in order to provide sufficient workforce for climate action. The COP29 conference will also set a special day for human capital for the first time, ensuring the central position of green talents in climate change. These actions may alleviate the shortage of green talents in the future.
Reference:








