Sustainable Roadmap Development Tool
The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) releases a jurisdictional sustainable roadmap development tool aimed at helping jurisdictions develop regulatory policies related to ISSB guidelines.
The ISSB has launched a series of educational materials and guidelines (such as guidelines for the adoption of sustainable standards in jurisdictions) to assist in the application of IFRS S1 and IFRS S2. The sustainable roadmap development tool translates the concepts in the sustainable guidelines into practical applications.
Related Post: ISSB Releases Preview of the Inaugural Jurisdictional Guide for the Adoption of ISSB Standards
Background of Sustainable Roadmap Development Tool
The ISSB believes that sustainable roadmap development tools are crucial for jurisdictions to adopt ISSB standards. The jurisdiction first familiarizes itself with ISSB standards, evaluates its sustainable regulatory policy system, and then uses sustainable roadmap development tools to set goals and identify key steps. Jurisdictions can also develop tools based on sustainable roadmaps to explore with stakeholders how to establish a sustainable disclosure ecosystem, helping businesses plan and implement sustainable disclosure.
The Sustainable Roadmap Development Tool aims to promote sustainable disclosure and provide investors with sustainable financial information. The legal and regulatory frameworks vary in different jurisdictions, and the roadmap will help regulatory agencies understand the impact of sustainable regulatory policies, as well as investors’ understanding of sustainable policies and how to achieve established goals.
Introduction to Sustainable Roadmap Development Tool
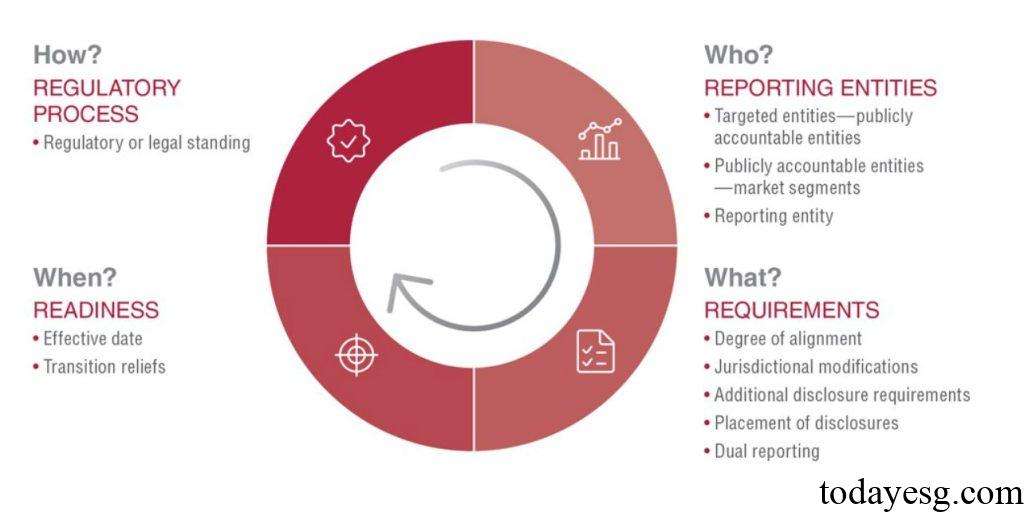
The ISSB has divided the sustainable roadmap development tool into the following sections based on the 11 jurisdictional characteristics mentioned in the Judicial Guide:
1 Regulatory process
The regulatory process section includes the legal, regulatory conditions and processes for applying ISSB standards, as well as communication mechanisms between regulatory agencies and stakeholders, specifically including:
- Regulatory or legal standing: Whether there are legal or regulatory requirements to apply ISSB standards or introduce sustainable disclosure requirements in other ways.
2 Reporting entities
The reporting entities section includes identifying which companies are subject to sustainable disclosure requirements and the objectives of the jurisdiction, including:
- Target entities: Applicable to entities in all or most jurisdictions.
- Market segments: Degree of applicability of sustainable disclosure requirements to entities.
- Reporting entity: Whether sustainable disclosure and financial disclosure belongs to the same entity.
3 Requirements
The requirements section includes the content and timing of sustainable disclosure, as well as additional requirements set by the jurisdiction, including:
- Degree of alignment: The degree of consistency between ISSB standards and local standards.
- Jurisdictional modifications: Whether the jurisdiction modifies the ISSB standards.
- Additional disclosure requirements: Whether additional disclosure is required outside of ISSB standards.
- Placement of disclosures: Whether sustainable disclosure reports and financial reports are provided simultaneously.
- Dual reporting: Whether dual reporting is based on local requirements and ISSB standards.
4 Preparations
The preparation section includes market assessment, a timeline for sustainable disclosure requirements, and whether the requirements will be implemented in stages, including:
- Effective date: Effective date of the sustainable disclosure regulatory policy.
- Transition relief: Phased implementation requirements and exemption time for sustainable disclosure.
Reference:
Roadmap Development Tool launched to support jurisdictions plan and design adoption roadmaps








