2024 Renewable Energy Report
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) releases 2024 Renewable Energy Report, which aims to analyze the development of the global renewable energy industry and related employment opportunities.
The IRENA believes that the development of renewable energy has changed the global energy structure and created new economic value and employment opportunities. These employment opportunities are necessary conditions for achieving a just and inclusive low-carbon transition.
Related Post: International Energy Agency Releases Emerging Market Clean Energy Report
Development of Renewable Energy Industry
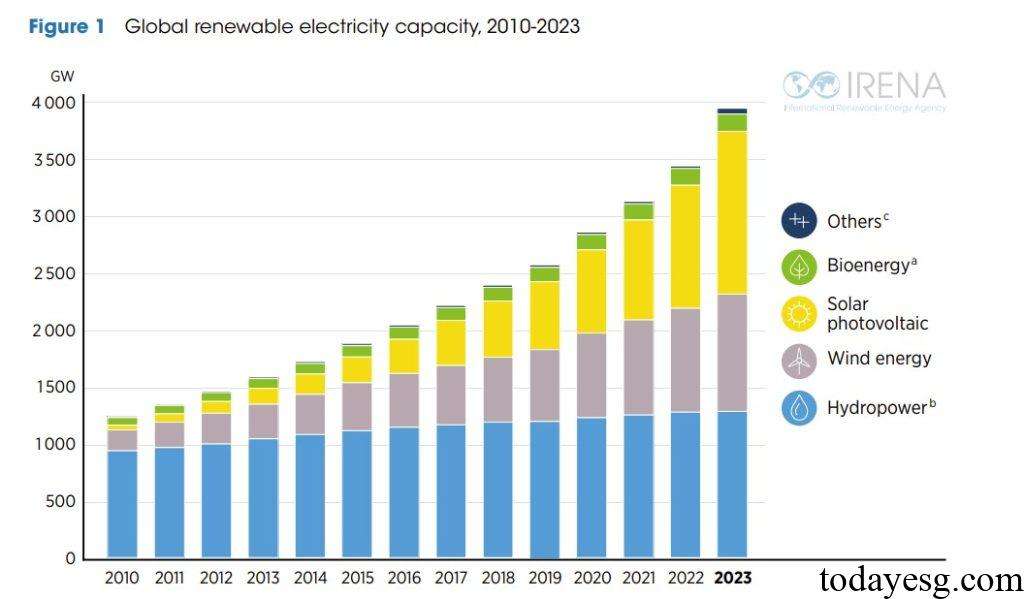
The global renewable energy generation capacity in 2023 is 3865GW, an increase of 14% compared to 2022. The photovoltaic industry ranks first in terms of power generation capacity, reaching 1411GW. The hydropower industry ranks second, reaching 1265GW. The wind energy industry ranks third, reaching 1017 GW. The capacity of the three renewable energy sources mentioned above accounts for 95% of the total, while other renewable energy sources is relatively small, such as bioenergy (149GW).
The development of renewable energy is uneven globally, for example, China’s investment in renewable energy far exceeds that of other countries in the world. The total investment in renewable energy in China from 2014 to 2023 was $1.572 trillion, three times that of the United States ($550 billion) and twice that of Europe ($785 billion). China is also the largest equipment manufacturing country in the wind and photovoltaic industries, with two-thirds of the world’s new wind and photovoltaic equipment installed by 2023. To achieve the COP28 conference’s goal of tripling global renewable energy by 2030, other countries need to increase their deployment efforts.
Renewable Energy Employment Opportunities
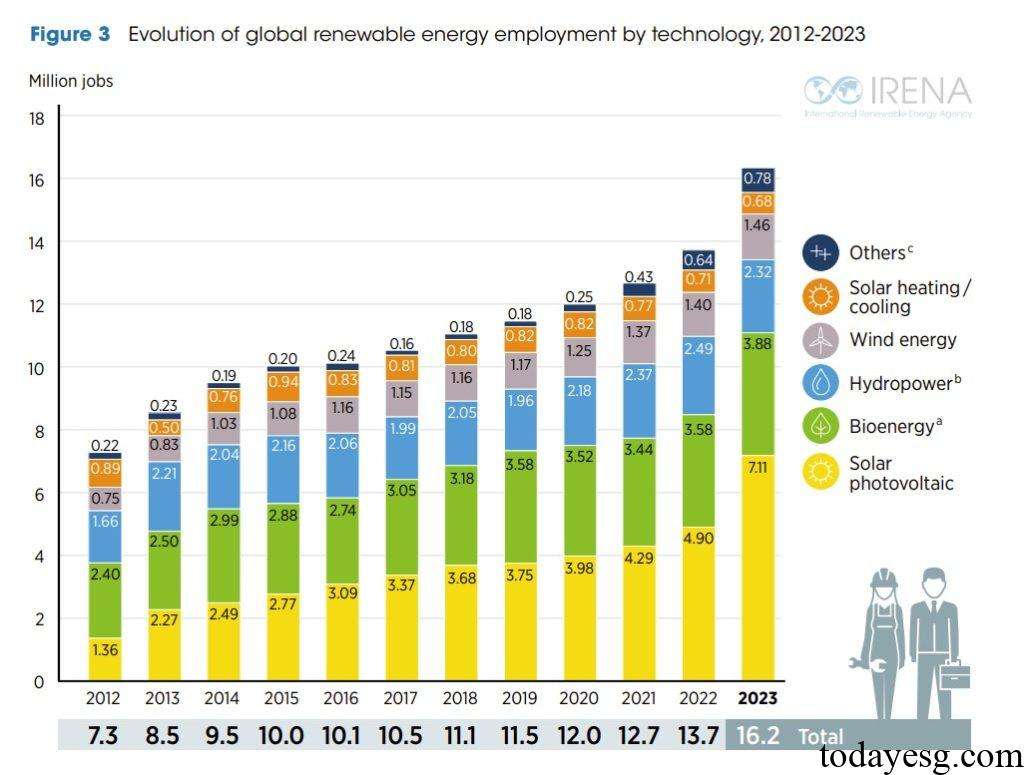
The global number of renewable energy jobs in 2023 is 16.2 million, an increase of 2.5 million compared to last year and 7.7 million compared to ten years ago. These positions are mainly provided by industries such as photovoltaics (7.11 million), bioenergy (3.88 million), hydropower (2.32 million), and wind energy (1.46 million). The global photovoltaic industry will add 347GW of power generation capacity in 2023, an increase of 74% compared to 2022, benefiting from a significant reduction in battery costs and policy support. The number of positions in China’s photovoltaic industry is 4.6 million, accounting for 65% of the global total.
The global wind energy industry adds 115GW of power generation capacity in 2023, with China adding 76GW, accounting for 66% of the global. The market share of Chinese companies in global wind energy equipment has increased from 17% in 2017 to 50% in 2022. There are 750000 jobs in China’s wind energy industry, accounting for 51% of the global.
The global hydropower industry adds 7GW of new capacity in 2023, and the growth rate is slowing down. Impact of hydropower industry projects on the environment and surrounding communities is the main reason for the decline. The decline in speed has led to a 16% decrease in the number of direct employment opportunities provided by the hydropower industry in 2023. There are 790000 jobs in China’s hydropower industry, accounting for 34% of the global.
In 2022, the global production of liquid biofuels reached 170 billion liters, an increase of 8 billion liters compared to 2021. The majority of employment opportunities in the biofuel industry are located in the agricultural supply chain, with developing economies providing raw materials and developed economies providing processing services. In 2023, there are 2.8 million jobs in the global liquid biofuel industry and 770000 jobs in the solid biomass industry.
Renewable Energy and Just Transition
With the global transition to renewable energy, existing and future labor forces need to receive training to acquire the skills required for emerging job opportunities. The International Labor Organization finds that the demand for labor with intermediate skills in the renewable energy sector is growing the fastest, such as photovoltaic panel installers and wind turbine technicians. These laborers will assist in the research, innovation, and development of energy transition.
The IRENA provides some suggestions for cultivating renewable energy workforce:
- Policy consistency: All countries need to implement coherent and coordinated policies to promote the development of renewable energy.
- Better data: Better data can help stakeholders provide timely and effective training on renewable energy.
- Skills intervention: Fair transition requires comprehensive educational methods such as vocational guidance, job matching, and social protection, and these skills development measures need to be incorporated into the transition framework.
- Vocational and technical education and training: Increase vocational and technical education and training to help students acquire practical experience and skills needed to engage in the renewable energy industry.
Reference:
Renewable Energy and Jobs: Annual Review 2024
ESG Advertisements Contact:todayesg@gmail.com







