Climate Bonds Taxonomy
This article introduces the Climate Bonds Taxonomy released by Climate Bonds Initiative (CBI).
The Climate Bonds Taxonomy aims to provide a classification guide for climate related assets, helping issuers and investors understand which investments can contribute to climate action, and how these investments are defined and measured. The Climate Bonds Taxonomy is also an important foundation for the establishment of the EU Taxonomy.
Related Post: The EU Releases a Report on the Application of EU Taxonomy
Background of the Climate Bonds Taxonomy
The financial industry has recognized the role of climate related investments in addressing global climate issues, but how to define and classify climate related assets is an urgent issue that needs to be addressed within the industry. Market participants need to use scientific classification methods to identify which financial assets contribute to the transition to a low-carbon economy. In 2013, the Technical Working Group and Industry Working Group under the Climate Bond Initiative jointly developed a classification system for climate bonds, namely Climate Bonds Taxonomy.
The Climate Bonds Taxonomy is based on the global warming target of 2 degrees Celsius set by the 2015 Paris Agreement, and identifies the assets needed for low-carbon and climate adaptive economies, while incorporating the research experience of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change and the International Energy Agency.
Contents of the Climate Bonds Taxonomy
The Climate Bonds Taxonomy uses a traffic light system to identify whether assets are consistent with decarbonization trajectories, where red represents inconsistency, orange represents consistency under specific criteria, and green represents consistency. In addition, gray represents that the Climate Bond Initiative is still developing classification methods for this type of asset. The certification of bonds by the Climate Bond Initiative is mainly based on the Climate Bonds Taxonomy, and if the bond is certified, a blue certification mark can be added.
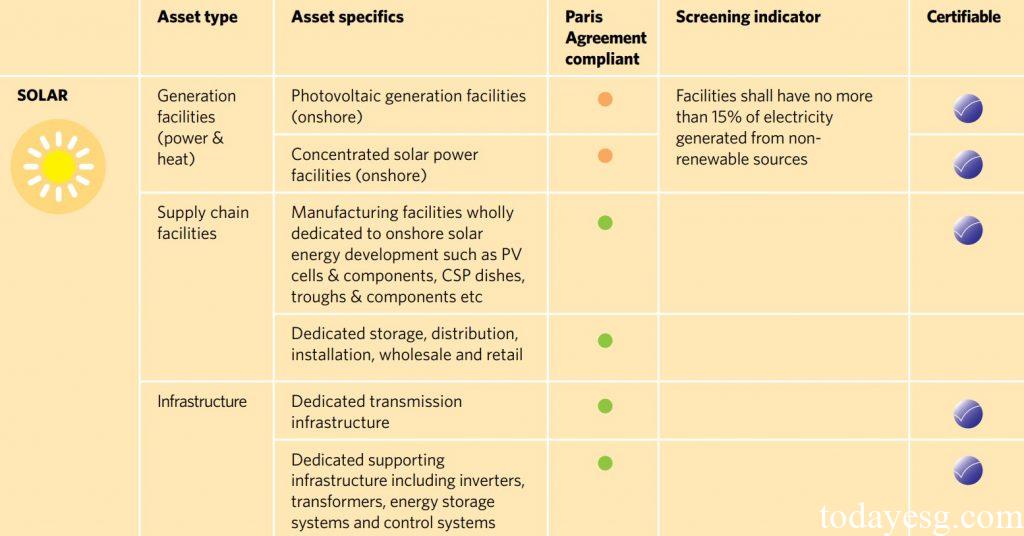
The Climate Bonds Taxonomy currently includes eight categories: energy, transport, water, buildings, land use & marine resources, industry, waste & pollution control, and information and communication technology. For each category, the classification system lists asset types, asset specifics, decarbonization trajectory compliant, and screening indicator.
For example, for solar under the energy industry, its asset types include generation facilities, supply chain facilities, and infrastructure. For generation facilities, they are divided into photovoltaic generation facilities (onshore) and concentrated solar power facilities (onshore), both of which are marked in orange and need to meet specific standards to be consistent with decarbonization trajectories. Every solar asset that meets the decarbonization trajectory can add a blue climate bond certification mark.
The Climate Bond Initiative plans to continuously follow up on the latest global developments in climate science and regularly revise and update the Climate Bonds Taxonomy, in order to play a positive role in the development of the international green bond industry.
Reference:








