California Cap and Trade Program
This article introduces the representative of the global compliance carbon market, the California Cap and Trade Program. The California Cap and Trade Program is one of the most comprehensive carbon pricing plans in the world, which can be interconnected with multiple carbon markets.
The goal of California Cap and Trade Program is to reduce carbon emissions to 60% of 1990 levels by 2030, 15% of 1990 levels by 2045, and achieve carbon neutrality. Currently, the California Cap and Trade Program covers 85% of California’s carbon emissions.
Related Post: Introduction to Global Compliance Carbon Market: EU Emissions Trading System
Structure of California Cap and Trade Program
The California Cap and Trade Program includes governance and carbon offsets.
Governance: The California Cap and Trade Program is managed by the California Air Resources Board, and its main responsibilities include monitoring greenhouse gas emissions, enacting laws, and overseeing quota allocation. The California Air Resources Board determines the upper limit of carbon market emissions and the number of quotas to be reduced each year, with a small portion of quotas allocated for free and the remaining quotas allocated through auctions. The auction event will be held quarterly, and the auction proceeds will be used for California’s carbon reduction plan. 70% of the quota for 2023 was allocated to enterprises through auction.
Carbon Offset: The California Cap and Trade Program allows the use of carbon offsets with quantity and quality limitations, which must come from projects under specific compliance compensation agreements. Enterprises can use carbon offsets to meet 8% of carbon emissions from 2013 to 2020, 4% of carbon emissions from 2021 to 2025, and 6% of carbon emissions from 2026 to 2030. Starting from 2021, the amount of funds offset from projects that do not directly generate environmental benefits in the State cannot exceed 50%.
Market Activities of California Cap and Trade Program
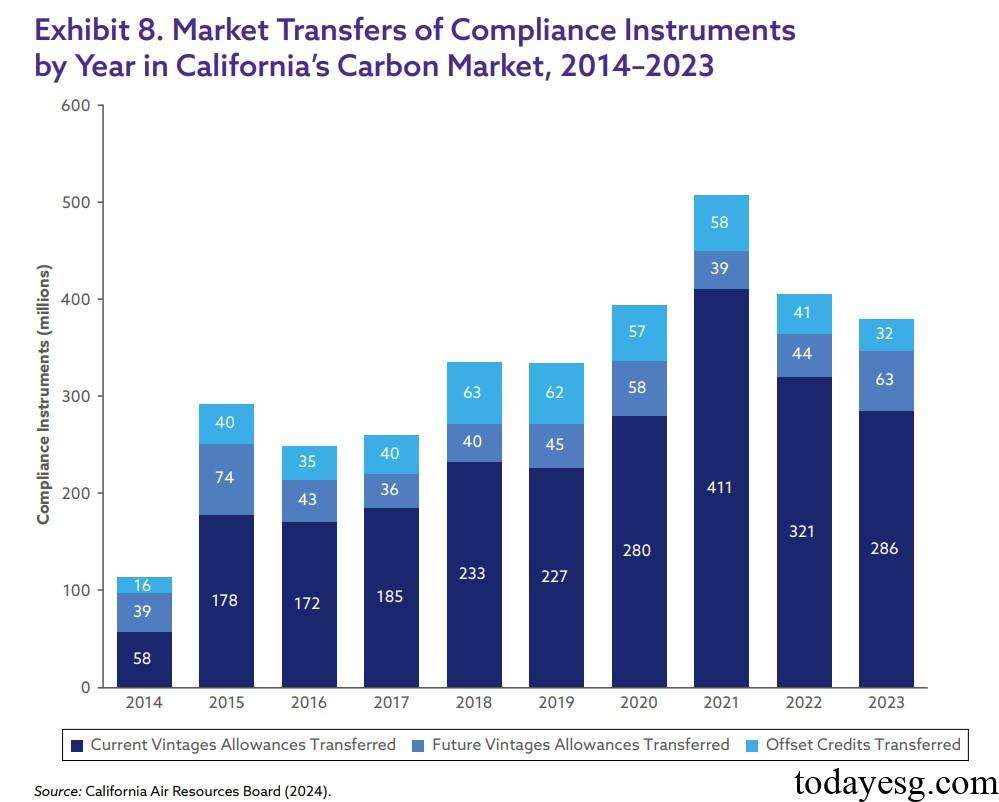
The increasing number of quota transfers under California Cap and Trade Program from 2014 to 2023 indicates active carbon market transactions. The California carbon market provides mechanisms for transferring current quotas, transferring future quotas, and using carbon credits, which can provide participants with diverse choices. The vast majority of market quota transfers are based on the current year, indicating that companies are actively aligning their quotas with the current year’s emissions. The proportion of carbon offset is low, which is in line with the mechanism of limiting the offset percentage. In recent years, the number of trading future quotas has been increasing, reflecting the market’s expectation of tightening the carbon emission cap in the future.
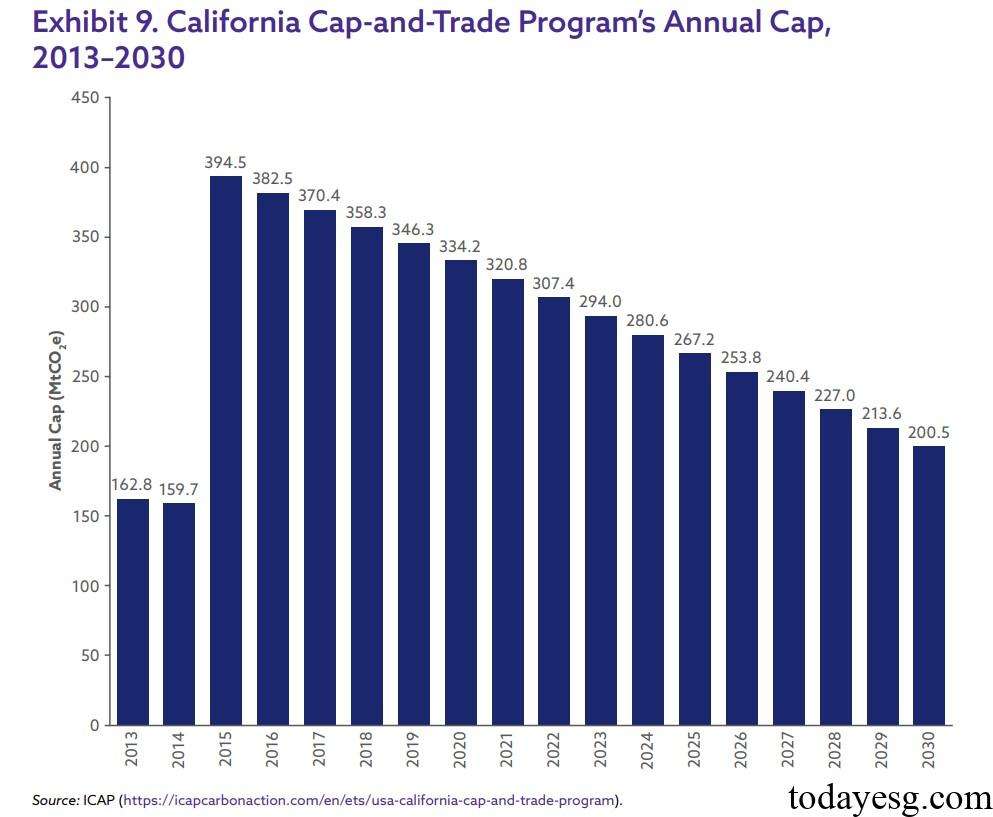
The annual cap of California Cap and Trade Program has been continuously decreasing since 2015. In the second compliance period (2015-2017), the cap decreased by 3.1% annually. In the third compliance period (2018-2020), the cap decreased by 3.3% annually. In the fourth compliance period (2021-2030), the cap decreased by 4% annually. Overall, the decline rate continues to accelerate.
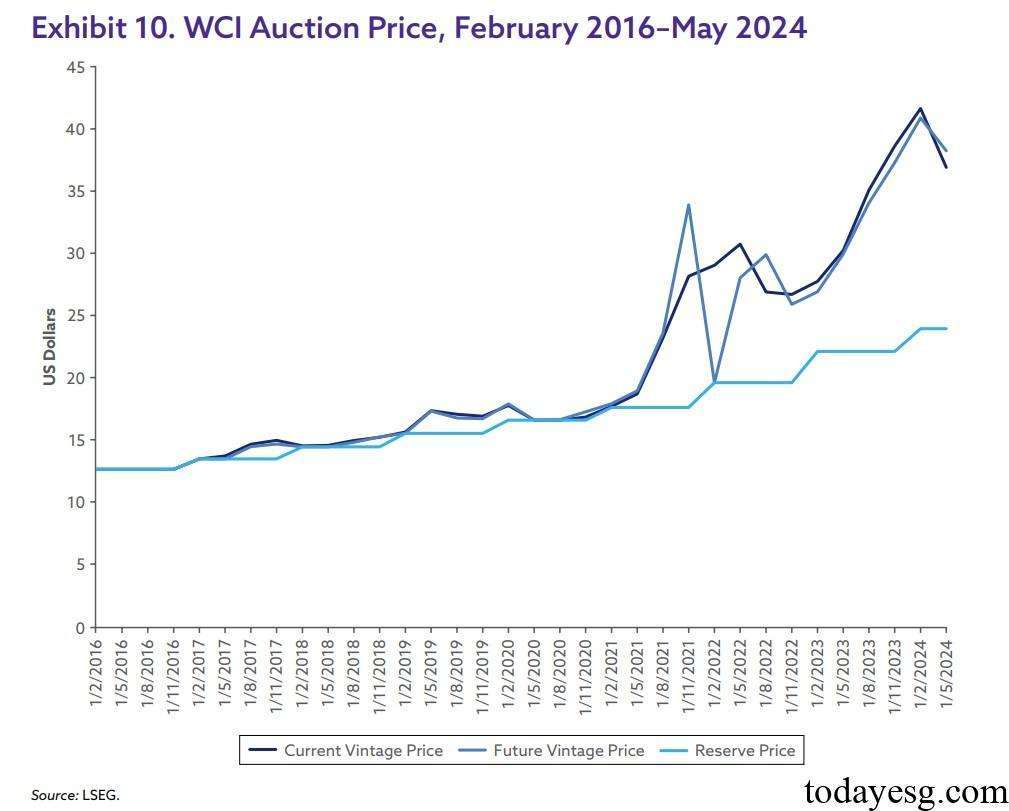
As of May 2024, the quota price for California Cap and Trade Program is $37, which has tripled in eight years. The California Cap and Trade Program also provides auction prices for future years to help businesses manage their carbon emissions expectations. Most of the time, the auction price for future years remains consistent with the current auction price.
Reference:
A Foundational Overview of Global Carbon Markets
ESG Advertisements Contact:todayesg@gmail.com








