Global Climate Related Financing Development
This article introduces the development of global climate related financing based on financial institutions.
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) released the Review on Aligning Finance with Climate Goals, which measures global climate related financing development from multiple dimensions, and financial institutions is an important dimension.
Related Post: Global Climate Related Financing Development Based on Financial Assets
Global Climate Related Financing Based on Financial Institutions
The OECD believes that financial institutions may hold multiple financial assets, which are important tools for achieving long-term climate goals. In response to climate change, some financial institutions have established the Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero, which is divided into three different parts: the Net Zero Asset Managers Initiative, the Net Zero Asset Owner Alliance, and the Net Zero Banking Alliance. Some investors have formed voluntary organizations, such as Paris Aligned Asset Owners and Climate Action 100+.
The OECD measures the global climate related financing development of financial institutions from the following perspectives:
Bank
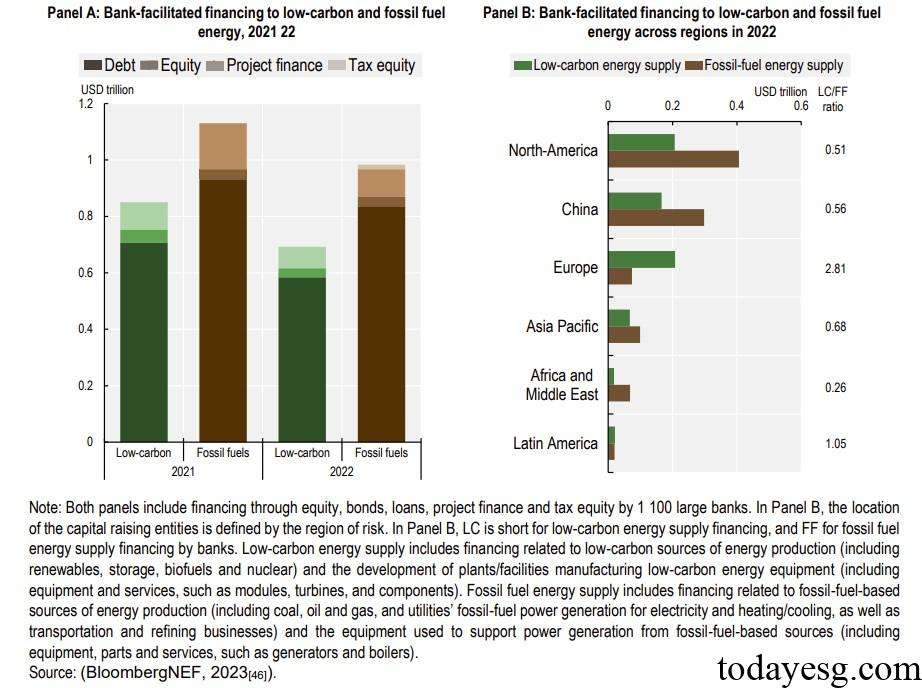
In 2022, the world’s top 1100 banks provided $0.7 trillion in financing for the low-carbon energy sector and $1 trillion in financing for the fossil fuel sector. In addition to direct financing, banks also participate in bond and equity underwriting activities. In 2022, members of the Net Zero Banking Alliance jointly underwrite $0.46 trillion in low-carbon energy assets and $0.52 trillion in fossil fuel assets. From a regional perspective, low-carbon energy financing accounts for a relatively high proportion in Europe and North America ($0.208 trillion and $0.207 trillion), while fossil fuel financing accounts for a relatively high proportion in North America and China ($0.406 trillion and $0.298 trillion).
Institutional Investor
Institutional investors include pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, insurance companies, asset management companies, etc. Taking pension funds as an example, in 2017, 7% of the equity assets of European pension funds were invested in the fossil fuel industry. In 2018, only 1% of the assets of the world’s top 100 pension funds were invested in low-carbon solutions. According to a survey conducted by the OECD in 2022 on 75 pension funds and 13 sovereign wealth funds, almost all institutional investors have a green asset ratio of less than 10%.
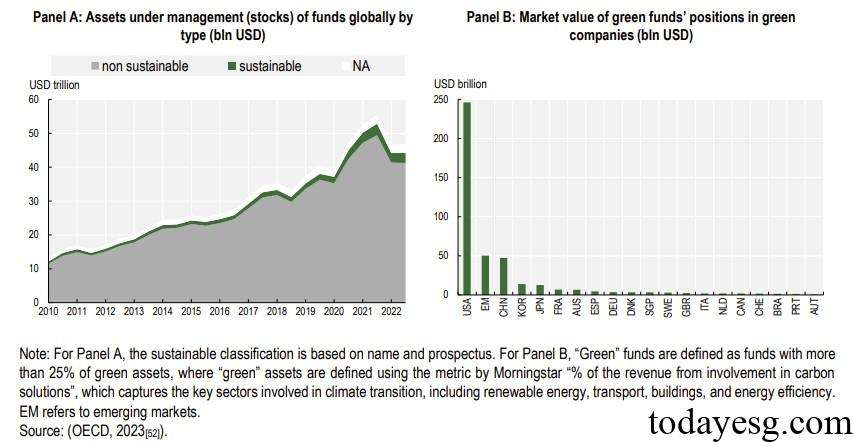
From the perspective funds, the size of sustainable funds in 2022 accounts for 6.2% of the total asset size, of which the fund’s green asset investment scale is $3.8 trillion, with the main investment locations being the United States and China. Green asset investment in emerging markets is relatively low, and if China’s green assets are not considered, the scale of green assets in emerging markets is less than 1%. Apart from stocks and bonds, institutional investors have less allocation of green assets. According to a 2020 study by OECD, institutional investors hold a total of $1.04 trillion in infrastructure assets, of which only $0.3 trillion belongs to green infrastructure investment.
Reference:








