Corporate Transition Classification System
This article introduces the corporate transition classification system released by Climate Bonds Initiative (CBI). The classification system aims to categorize companies based on their transition goals, progress, and credibility, helping financial institutions measure the transition risks they face and adjust their lending, investment, and other business activities accordingly.
Transition financing is an important action taken by financial institutions to promote net zero emissions in the real economy. Many net zero initiative organizations, such as the Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero and the Institutional Investors for Net Zero, have also developed transition financing frameworks. However, due to the fact that most enterprises are still in the early stages of their transition plans, there are difficulties in applying these frameworks.
Related Post: Introduction to the Transition Assessment Guidelines of Climate Bond Initiative
Introduction to Corporate Transition Classification System
In order to assist financial institutions in determining the stage of corporate transition and address existing issues in the transition framework, the Climate Bond Initiative has developed a corporate transition classification system based on the Transition Finance Mapping. This classification system can help financial institutions understand the complexity and differences of existing frameworks, and extract core indicators from them.
The Climate Bond Initiative has adopted the concept of Maturity Ladder, which was originally created by the IIGCC to map different categories of corporate transition plans into the ladder for classification and aggregation of different companies. This concept summarizes the consensus of the Climate Bond Initiative on a large number of corporate transition categories and frameworks, and adds some different categories to reflect the substantive performance of current corporate transition plans.
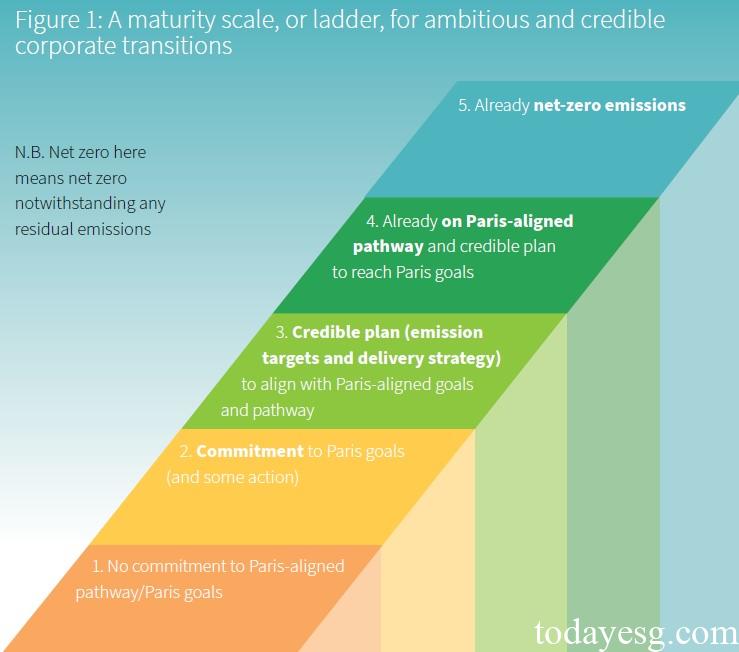
The enterprise transition classification system divides transition plans into five different categories, each measured by five indicators: commitment, emissions targets, delivery strategy, governance, and performance. When a company meets some of its goals, it can be classified into one of the five categories of transition plans:
- No Action: The company has not committed to complying with the goals of the Paris Agreement and has no relevant net zero targets, governance, etc. This category is the lowest in the net zero classification.
- Committed: The company has committed to complying with the goals of the Paris Agreement and has established short-term emission targets and internal governance processes, which are higher than the No Action category.
- Aligning: The company has committed to complying with the goals of the Paris Agreement and has established comprehensive emission targets and decarbonization plans, while also having internal governance processes in place. In terms of performance, the company has achieved some of the planned goals and the actual emission data meets expectations. This category is approaching the carbon reduction path of the Paris Agreement.
- Aligned: Based on the previous category, the actual carbon emission data of the enterprise has reached a credible benchmark condition, and the decarbonization path of the enterprise has been consistent with the decarbonization path of the Paris Agreement.
- Net Zero: The enterprise has achieved net zero, which is the highest category in the net zero classification.
Application of Corporate Transition Classification System
The Climate Bond Initiative believes that financial institutions can classify a company’s net zero plan based on the above classification system and use it for services such as loans, investments, and consulting. For example, the first two categories of corporate financing cannot be considered as transitional finance or green finance. All three categories can be considered as green finance, among which corporate financing that has already achieved net zero cannot be considered as transitional finance. These classification methods will provide a basis for financial institutions’ net zero financing business.
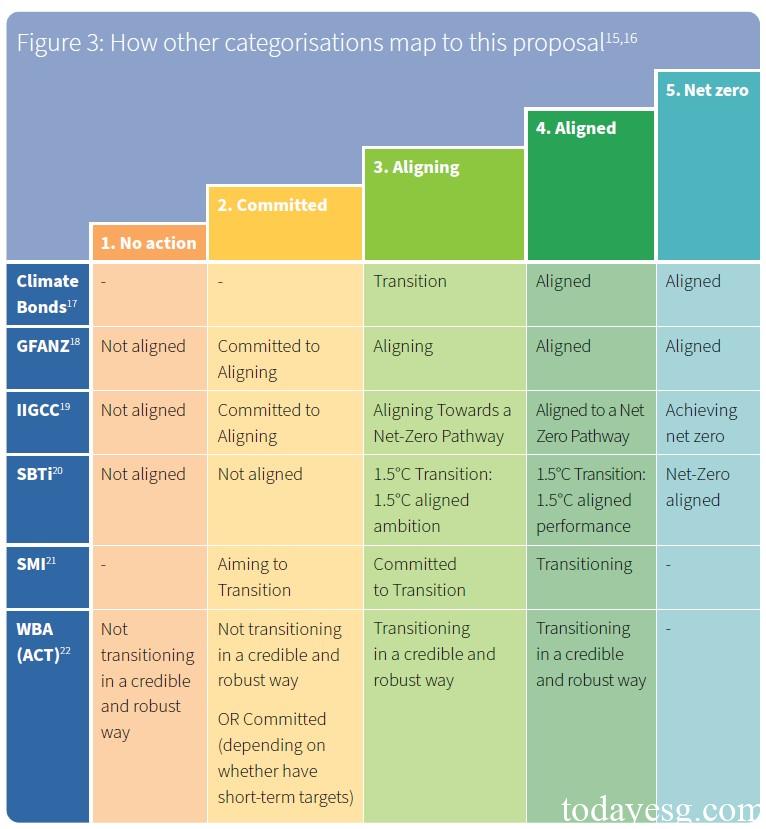
In order to improve the interoperability of different transition plans, the Climate Bond Initiative has mapped some commonly used net zero related frameworks into classifications, which come from the Glasgow Net Zero Finance Alliance, the Institutional Investor Group on Climate Change, the Science Carbon Targets Initiative (SBTi), the Sustainable Markets Initiative, and Assessing Corporate Transition. When financial institutions refer to these net zero frameworks, they can also correspond them to the enterprise transition classification system to avoid duplication of work.
Reference:
Climate Bonds Initiative Navigating Corporate Transitions
ESG Advertisements Contact:todayesg@gmail.com








