China National Carbon Emissions Trading Scheme
This article introduces the representative of the global compliance carbon market, the China National Carbon Emissions Trading Scheme, which is the carbon market with the largest absolute emissions coverage in the world.
The China National Carbon Emissions Trading Scheme covers 5 billion tons of carbon dioxide, accounting for over 40% of China total carbon dioxide emissions. From 2013 to 2016, China established carbon market pilot projects in eight regions and ultimately integrated these pilot projects into a national carbon emissions trading scheme, covering over 2000 power industry companies with carbon emissions exceeding 26000 tons of carbon dioxide.
Related Post: Introduction to Global Compliance Carbon Market: EU Emissions Trading System
Structure of China National Carbon Emissions Trading Scheme
The China national carbon emissions trading scheme includes coverage, carbon allowance and carbon offset.
Coverage: China plans to reduce its carbon emissions per unit of GDP to 82% of 2020 levels by 2025 and 35% of 2005 levels by 2030 through the national carbon emissions trading scheme, ultimately achieving carbon neutrality by 2060. The emission limit set by the national carbon emissions trading scheme from 2019 to 2020 is 4.5 billion tons of carbon dioxide, and the emission limit from 2021 to 2022 is 5 billion tons of carbon dioxide. At present, China national carbon emissions trading scheme mainly focuses on the power industry, and plans to expand its coverage to the petrochemical, chemical, construction, steel, non-ferrous metals, paper and aviation industries.
Carbon Allowance: China national carbon emissions trading scheme mainly provides carbon allowances through free allocation and adjusts them based on different types of enterprises. Over time, regulatory agencies may gradually tighten free quotas and instead provide them through auctions. The China National Carbon Emissions Trading Scheme provides flexibility through bank lending, allowing companies to carry forward unused quotas since 2019 to encourage them to plan carbon reduction activities.
Carbon Offset: China national carbon emissions trading scheme allows companies to use carbon offsets, but with restrictions. Enterprises can use the China Certified Emission Reduction quota, and their usage cannot exceed 5% of the total emissions. These carbon offsets comply with the standards set by the National Center for Climate Change Strategy and International Cooperation.
Market Activities of China National Carbon Emissions Trading Scheme
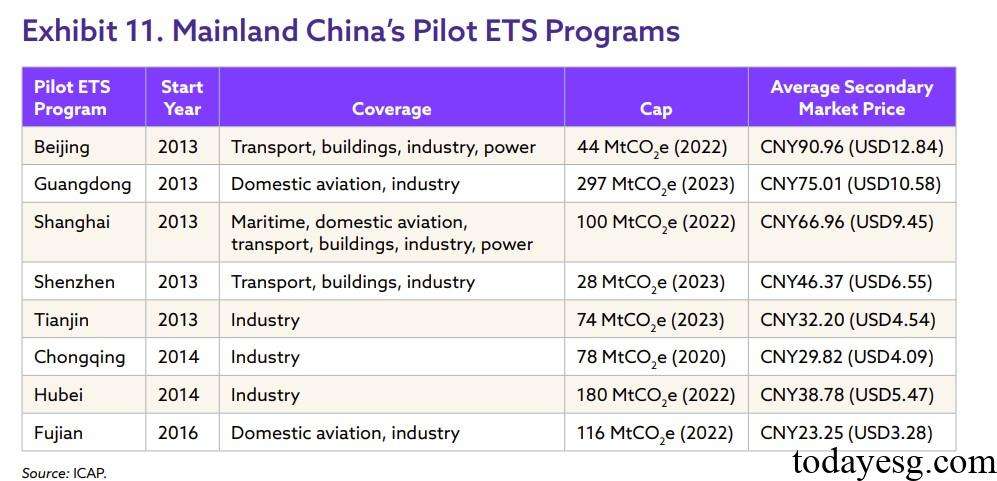
Before the establishment of China national carbon emissions trading scheme, there were significant price fluctuations in pilot carbon markets from different regions, and there were significant differences in carbon prices between different regions. This may be due to the diversity in carbon pricing across regions, but as the overall carbon market is established, these carbon prices gradually converge, and different carbon markets respond to policy incentives.
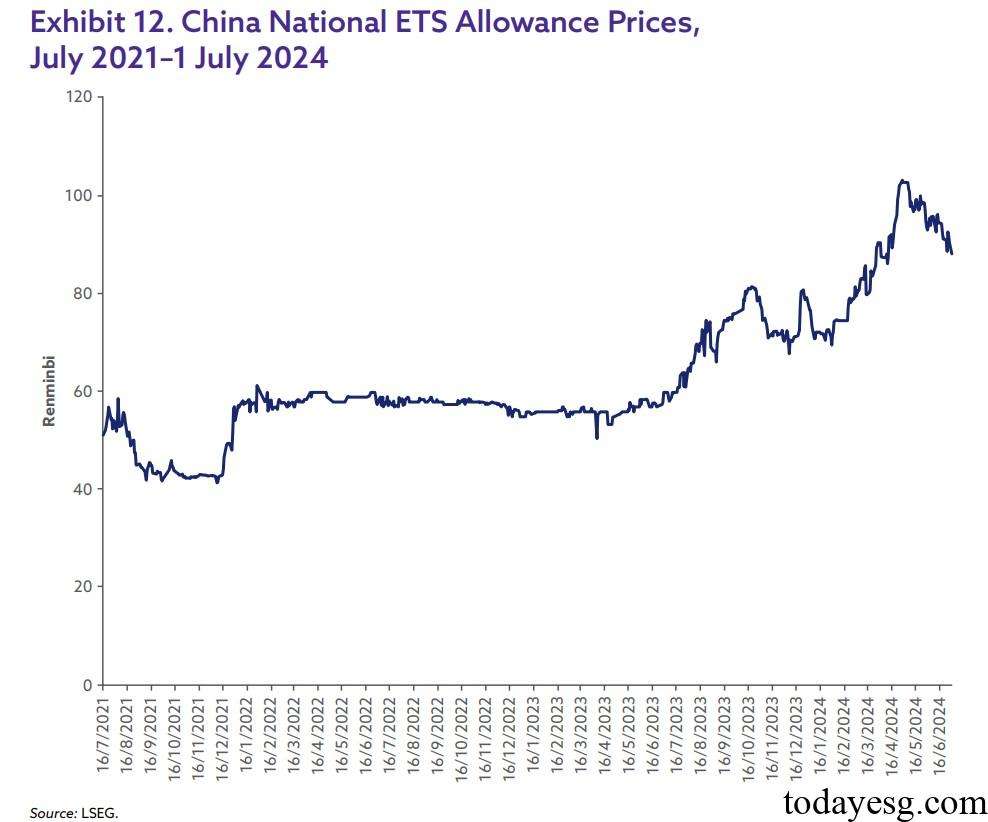
Since the launch of China national carbon emissions trading scheme in 2021, carbon prices have gradually increased, which may be due to the tightening of carbon emission limits and stricter policy expectations in the future. Compared to the European carbon market (such as the EU Emissions Trading System), China carbon prices are still at a low level, and as the carbon market continues to mature in the future, carbon prices may continue to rise.
Reference:








