Global Carbon Market Report
The CFA Institute releases a global carbon market report aimed at analyzing the mechanisms, roles, and improvement of the global carbon market.
The CFA Institute believes that investors need to understand the global carbon market in order to analyze its potential investment and trading opportunities.
Related Post: HKEX Releases Carbon Market Report
Overview of Global Carbon Market
The global carbon market is an effective tool for determining carbon pricing and supporting net zero targets, aimed at achieving carbon reduction goals by limiting the total amount of carbon emission quotas. According to the International Carbon Action Partnership, 58 jurisdictions worldwide have established carbon markets by 2024. According to World Bank, the global carbon market will cover 19% of carbon emissions by 2024, up from 7.9% in 2020.
For the investment industry, the global carbon market plays the following roles:
- Support global climate goals: Investors can contribute to global climate action by participating in the carbon market.
- Provide new investment opportunities: The carbon market provides new investment strategies and products that have low correlation with traditional assets.
- Participate in financial analysis and valuation: Enterprises incorporate carbon emission costs into their financial performance, market valuation, and influence investment returns.
The global carbon market can be divided into Compliance Carbon Market and Voluntary Carbon Market, with the former being the largest with a global trading value of 881 billion euros in 2023. There are currently 58 compliance carbon markets worldwide, and several representative compliance carbon markets include:
- European Emissions Trading System (EU ETS): highest total trading value.
- California Cap and Trade Program: highest coverage percentage.
- China National Emissions Trading System (China National ETS): highest absolute emissions.
The two basic elements of a compliance carbon emissions market are carbon allowance and carbon offset. The carbon market issues carbon quotas to enterprises through licenses, while the voluntary carbon market only provides carbon offsets. Regulators typically set a threshold for companies, which may be related to the industry and their historical carbon emissions. Regulators will allocate a portion of carbon quotas to companies free of charge, while the other portion will be allocated through auctions. When a company’s emissions exceed the threshold, it needs to purchase additional quotas through auction or trading.
The voluntary carbon market is a supplement to the global carbon market, allowing companies to purchase carbon credits to offset their emissions. There are various types of projects in the voluntary carbon market, each of which uses different methods to quantify its emission reductions. The projects must be validated according to established standards in order to generate carbon credits. Despite the rapid development of the voluntary carbon market, there are still challenges in its credibility, transparency, and other aspects. Some voluntary carbon market working groups have been established to improve the standards of the market.
Global Carbon Market and Net Zero
The CFA Institute believes that the global carbon market is an effective tool for achieving net zero emissions, and the role of the carbon market includes:
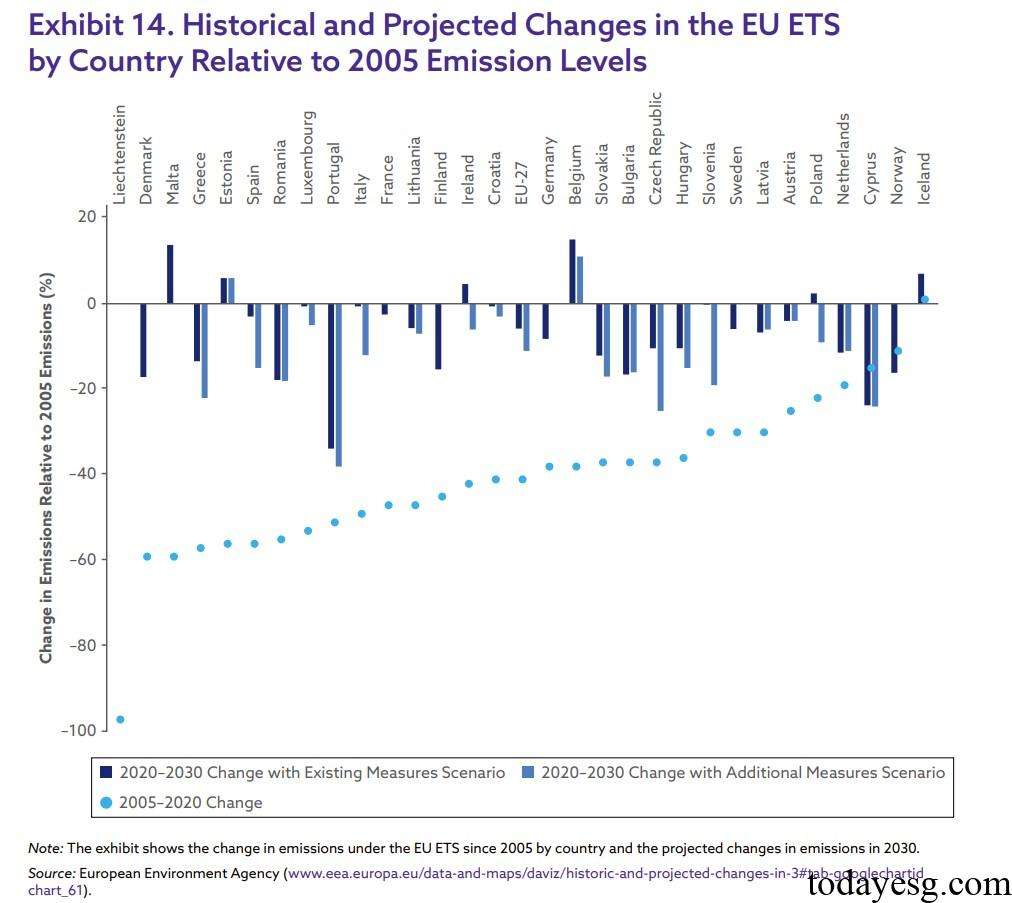
- The global carbon market can reduce carbon emissions and promote consistency between carbon reduction and the net zero path: Countries can use the carbon market system to set overall emission limits in order to develop emission reduction plans. From 2005 to 2020, carbon emissions in EU countries have generally decreased by 40% to 60%.
- The customized mechanism of the global carbon market can encourage companies to reduce carbon emissions: Carbon market provides a pricing mechanism for carbon emissions, allowing companies to include the cost of carbon emissions in their production costs and providing them with the motivation to reduce emissions.
- The global carbon market allows companies to participate in the carbon reduction and expand the scope of carbon reduction: the voluntary carbon market provides opportunities for companies that are not subject to compliance carbon market regulation to participate in carbon reduction.
- The global carbon market has promoted the development of green technology and green finance: the carbon market encourages enterprises to achieve green transition in the medium and long term, which can accelerate the development of markets such as green technology and green energy, and improve the efficiency of fund allocation.
How to Improve Global Carbon Market
The CFA Institute believes that there is room for improvement in the current global carbon market, including:
- Set a reasonable upper limit: In the absence of reliable data, setting an initial emission limit for the carbon market may result in a mismatch between the total quota and actual emissions, affecting the carbon emission costs of enterprises.
- Price fluctuations: Carbon prices in the carbon market may experience significant fluctuations due to participants’ expectations, policy changes, and quota allocation methods. Solutions include increasing carbon market products.
- Market development differences: There are significant differences in emission reduction targets among different carbon markets, making it difficult to compare. This is directly related to factors such as energy policies and economic structures of various countries.
- Market segmentation: there is a carbon leakage problem between different carbon markets, which may reduce the competitiveness of enterprises. The global carbon market system fails to exchange carbon quotas internally, affecting the efficiency of resource allocation.
Reference:








