Introduction to Carbon Dioxide Removal
This article introduces the definition, classification, and application of Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR).
Related Post: Carbon Capture and Storage: Definition, Classification, and Application
Carbon Dioxide Removal Definition and Classification
Carbon Dioxide Removal refers to the removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to ensure that the carbon budget for a temperature increase of 1.5 degrees Celsius is not exceeded. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) defines Carbon Dioxide Removal as the human activity of removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and permanently sequestering it in geology, land, or oceans. Carbon Dioxide Removal includes the capture and storage of carbon dioxide by existing and potential human activities but does not include natural removal by non-human activities.
As an important means of decarbonization, the main functions of Carbon Dioxide Removal include:
- Reduce net carbon dioxide or greenhouse gas emissions in the short term.
- Balance the remaining emissions that are difficult to reduce and achieve net zero carbon dioxide or greenhouse gases in the medium term.
- Achieve net negative emissions through large scale deployment of Carbon Dioxide Removal technology in the long term.
The IPCC believes that carbon capture and storage does not belong to Carbon Dioxide Removal technologies, as their application can at most achieve carbon neutrality, meaning they do not release new carbon dioxide but cannot reduce it. There are multiple categories of Carbon Dioxide Removal, which vary greatly in terms of technological development, storage capacity, storage time, cost, and benefits. The common Carbon Dioxide Removal technologies in the current market include:
- Bioenergy with Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage.
- Direct Air Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage.
- Land use.
- Afforestation.
- Biochar.
- Soil carbon management.
- Enhanced weather.
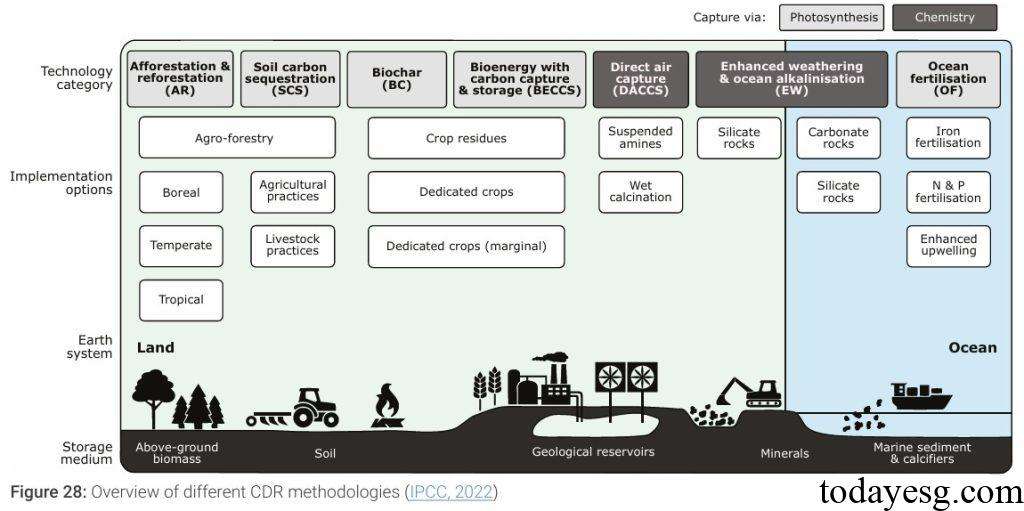
Carbon Dioxide Removal Application
The IPCC 1.5 ° C scenario proposes several of the most used Carbon Dioxide Removal methods, including:
- Bioenergy with Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage: Based on plant removal of carbon dioxide, the process involves planting plants and then burning them to produce energy. The carbon dioxide produced during the combustion process is captured and stored. It is expected that this technology will be rapidly deployed starting in 2035 and can remove 3.8 billion tons of carbon dioxide annually by 2050.
- Direct Air Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage: Capture carbon dioxide from the air and generate a pure carbon dioxide stream. This technology can use liquid adsorbents in high-temperature environments or solid adsorbents in low-temperature environments. It is expected that this technology will be rapidly deployed starting in 2040, and by 2050, it will be able to remove 1 billion tons of carbon dioxide annually.
- Land use and afforestation: Currently the most widely used Carbon Dioxide Removal method, accumulating carbon emissions in soil and plants. It is expected that this technology will experience significant growth by 2035 and be able to remove 3.4 billion tons of carbon dioxide annually by 2050.
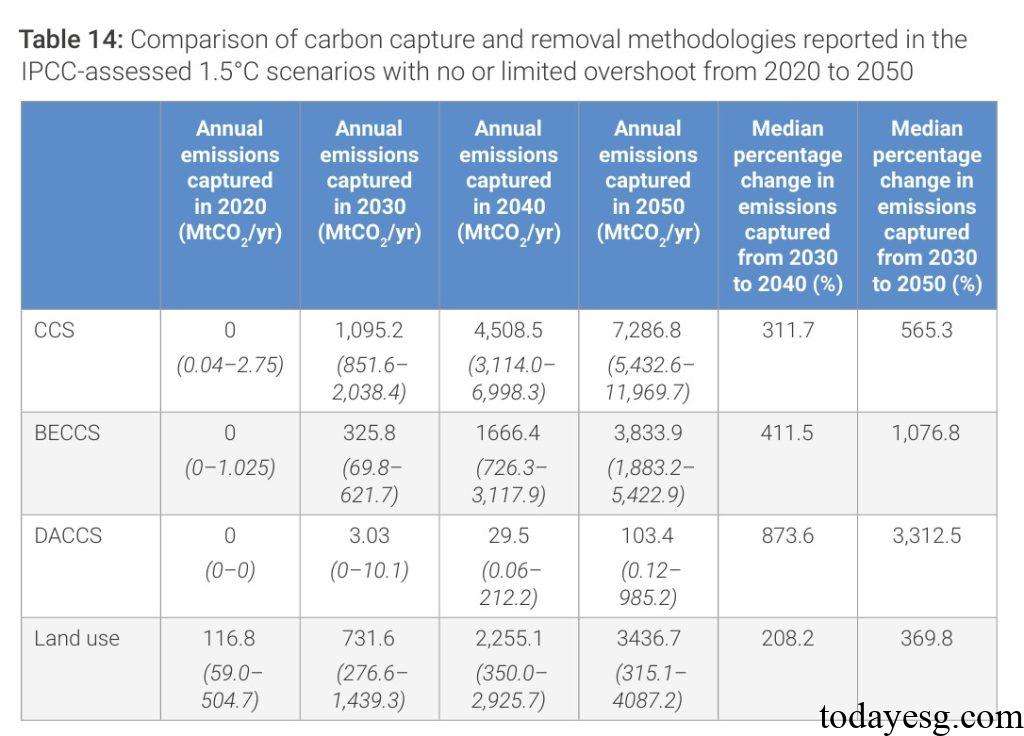
Although land use and afforestation are currently the largest Carbon Dioxide Removal methods, these carbons will not be permanently sequestered. As global temperatures rise and climate change events increase, carbon stored on land may be released back into the atmosphere. Therefore, the application of Carbon Dioxide Removal still needs to be continuously developed from multiple technologies to reduce the risks associated with a single technology.
Reference:





