Global ESG Metrics Report
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) releases global ESG metrics report, aimed at analyzing the scope and characteristics of ESG metrics used by global ESG data and rating providers.
The OECD believes that high-quality ESG metrics can help investors, businesses, and regulators accurately assess sustainability related impacts, risks, and opportunities, and effectively allocate capital to economic activities that align with sustainable development goals.
Related Post: Bloomberg Releases ESG Data Report
Introduction to Global ESG Metrics
ESG metrics measure a company’s performance across a range of sustainability factors and are essential elements of ESG data products. The global ESG data product market size has exceeded $1.5 billion by 2023 and is growing at a rate of over 20% annually. According to estimates, the cost of using ESG data is 2.5 times higher than the cost of traditional financial data. The transparency and quality of ESG metrics are important foundations for ESG data to meet the needs of stakeholders.
Investors use ESG metrics to measure a company’s sustainable performance and monitor the sustainability characteristics of their investment portfolios. Enterprises use ESG metrics to disclose sustainability related risks and opportunities. Regulators use ESG metrics to manage the disclosure of information by companies and investors. Numerous jurisdictions have issued ESG data and rating regulatory policies to improve information quality. For example, Hong Kong has issued code of conduct of ESG rating and data product supplier, requiring providers to voluntarily comply.
Research on Global ESG Metrics
To evaluate the characteristics of global ESG metrics, OECD collects over 2000 ESG metrics from eight ESG rating products worldwide and conducts empirical research based on the frameworks of the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). These ESG rating products have a market share of over 80%, covering a range of companies from 2000 to 20000.
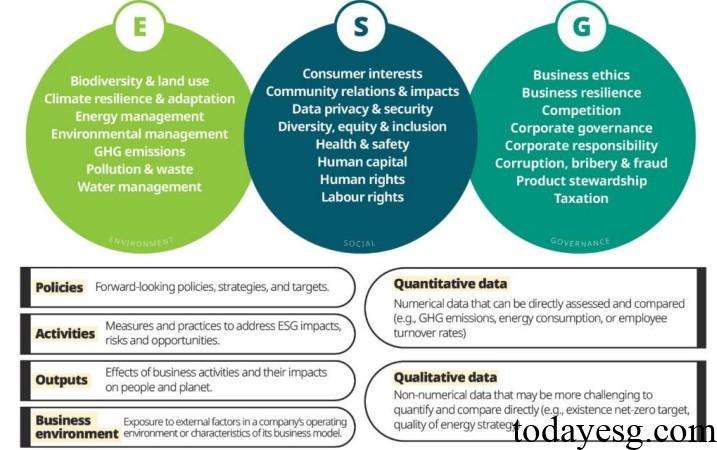
The OECD finds that the number of ESG metrics in eight ESG rating products ranges from 111 to 573. 50% of products use ESG metrics specific to certain themes, such as adding additional biodiversity indicators for food companies. To measure the ESG performance of different indicators, OECD divides them into 23 themes, including 7, 8, and 7 for environment, society, and governance, respectively. OECD categorizes ESG metrics into the following types based on their characteristics:
- Policy-based metrics.
- Activity-based metrics.
- Output-based metrics.
- Business environment metrics.
Characteristics of Global ESG Metrics
OECD finds that each ESG rating product provides 87 environmental indicators, 74 social indicators, and 83 governance indicators on average. The most common indicators are corporate governance (35), business ethics (24), environmental management (20), greenhouse gas emissions (19), and pollution (18). The least common indicators are biodiversity (5), business resilience (5), community relations (4), taxation (2), and competition (1).
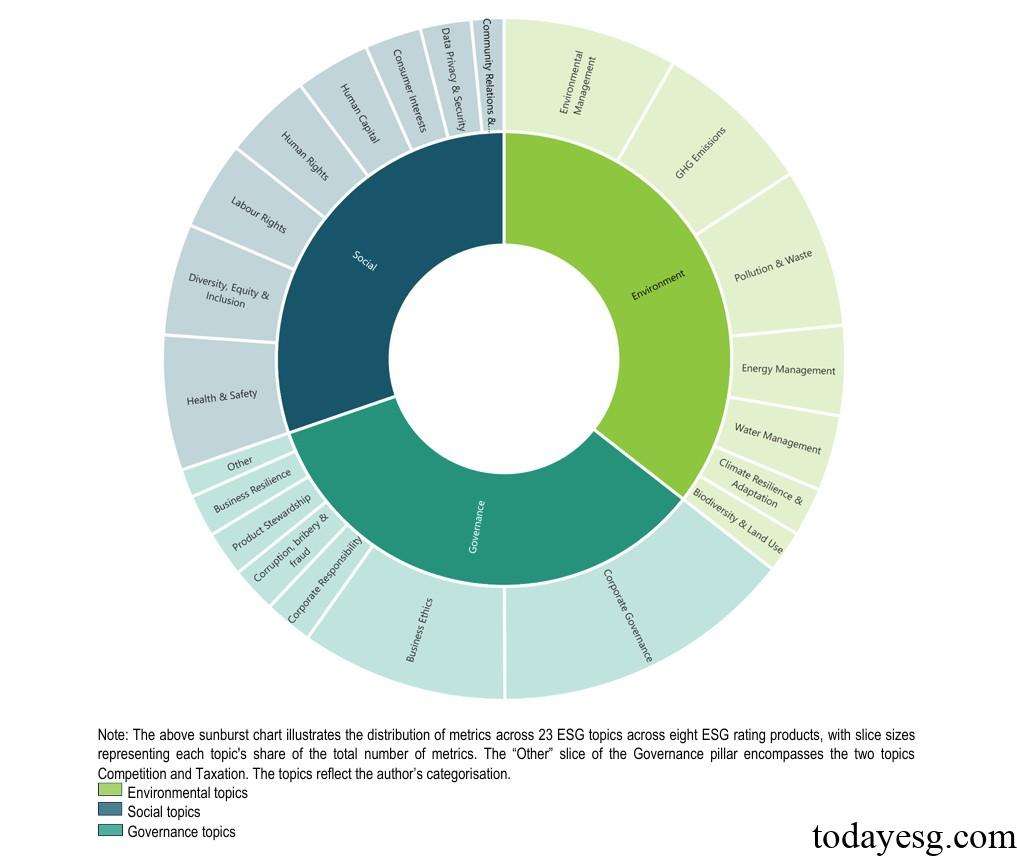
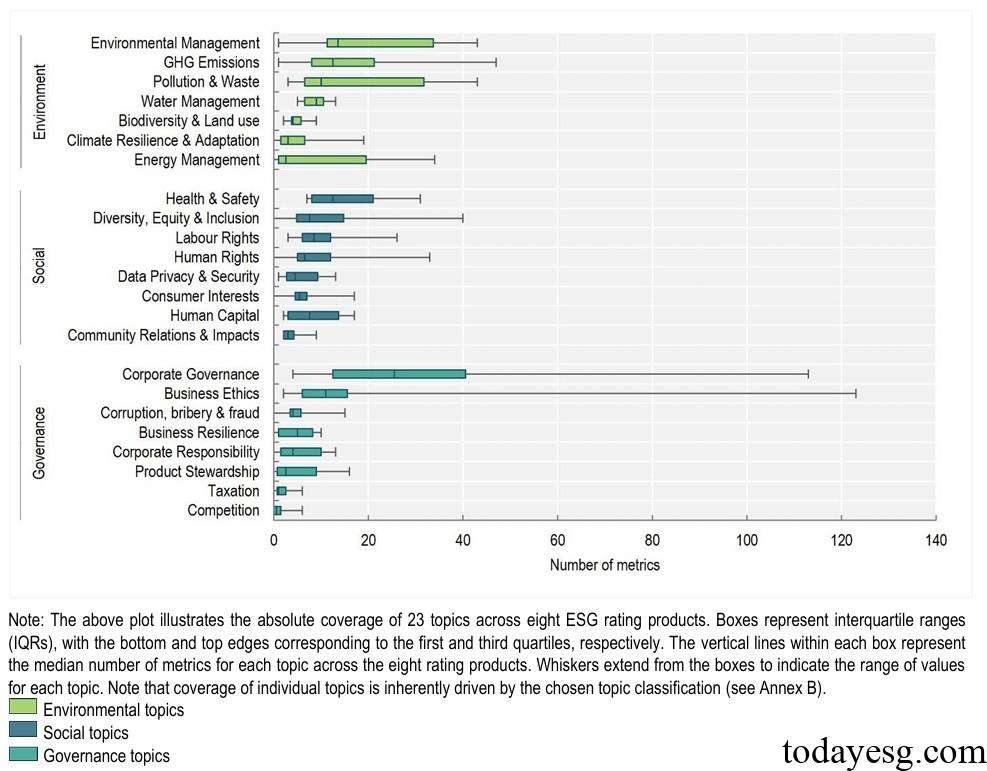
There are differences in the evaluation of ESG metrics among different ESG rating products. Some ESG rating products have over 100 ESG metrics in governance, but less than 60 ESG metrics in environmental and social aspects. Corporate governance and business ethics are the two most distinct ESG indicator themes, and information is relatively easier to collect and is also common in traditional rating products. The application of biodiversity indicators is relatively minimal, making it difficult to measure sustainable risks and opportunities.
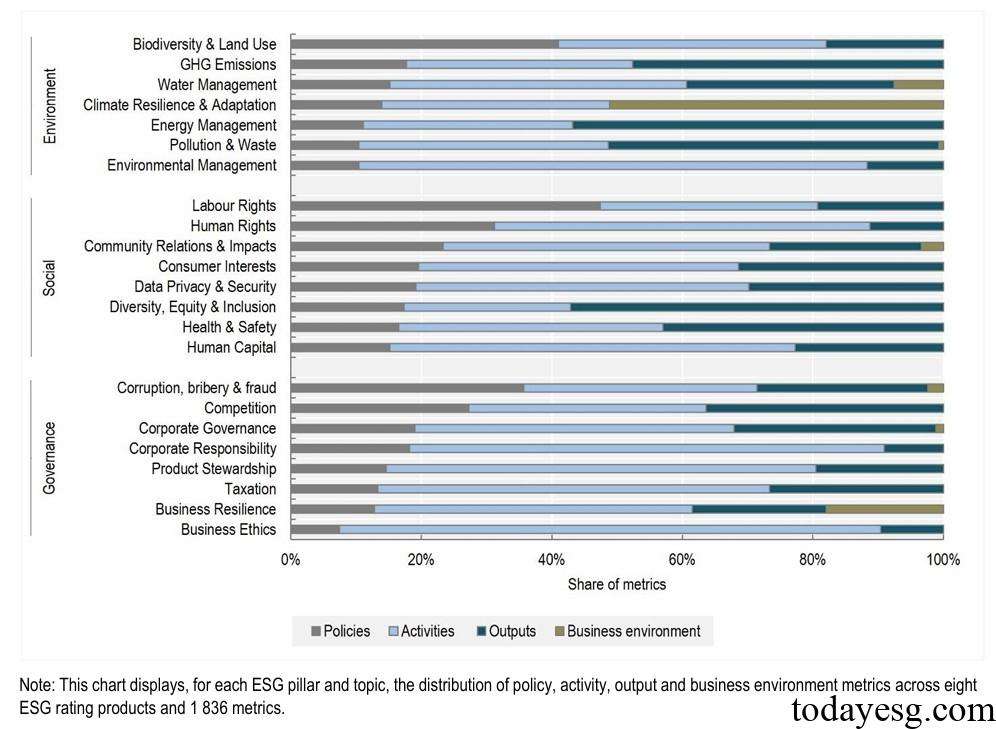
In the classification of the OECD, ESG metrics are mainly divided into activities (50%), output (30%), strategies (18%), and business environment (2%), and the information used to evaluate ESG performance mainly comes from enterprises. There are differences in the distribution of different types of indicators in the environment, society, and governance. For example, output-based indicators have a higher proportion in the environment, while activity-based indicators have a higher proportion in governance. From both qualitative and quantitative perspectives, 72% of ESG metrics are qualitative indicators and 28% are quantitative indicators.
Reference:








