2024 Global Blended Finance Report
Convergence, the global blended finance network, releases its 2024 report on global blended finance, aimed at analyzing the development of global blended finance market as well as climate blended finance market.
Convergence believes that the total global climate-related financing has increased by 120% in the past year, reaching a historic high, indicating that blended financing can attract funding for climate action. As the world approaches the key sustainable development goals by 2030, blended financing will become an important channel to fill the financing gap.
Related Post: Climate Policy Initiative Releases Global Climate Finance Report
Global Blended Finance Market Development
In 2023, the total global blended finance reached a historical high of $23.2 billion, an increase of nearly $10 billion compared to 2022. This growth mainly comes from the development of climate blended financing (from $8 billion in 2022 to $18.3 billion in 2023), and non-climate blended financing remaining $4.9 billion. The proportion of climate blended finance in global blended finance has reached 80%, surpassing the peak of 74% in 2021 and reaching a historical high.
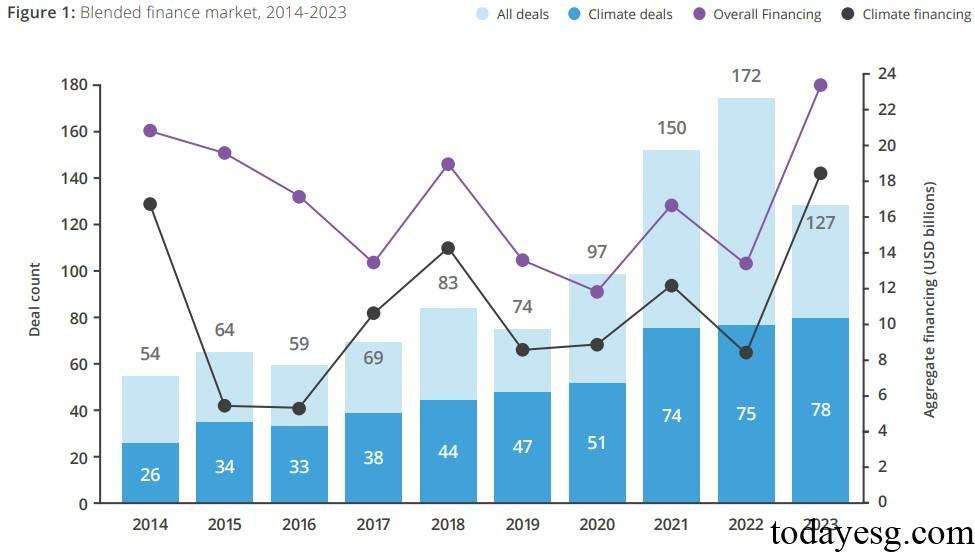
The Convergence database recorded a total of 1233 blended finance deals with a total value of $231 billion. Climate blended financing reached $132 billion, accounting for 57% of the total value. In the past three years, there have been 150, 172, and 127 global blended finance deals, among which 74, 75, and 78 climate blended finance deals have remained relatively stable.
From the analysis of the funding sources, the private sector’s financing amount reached $6 billion in 2023, which is three times that of 2022 ($2.1 billion). According to historical data analysis, $1 in concession capital can mobilize $2.2 in private sector financing, and this value increases to 2.65 in 2023. In 2023, the financing amount of Development Finance Institutions (DFIs) and Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) reached $4.7 billion, an increase of $1.7 billion compared to 2022, also reaching a historical high. The scale of Official Development Assistance (ODA) reached $1.1 billion, the lowest level in nearly four years.
Global Climate Blended Finance Market Development
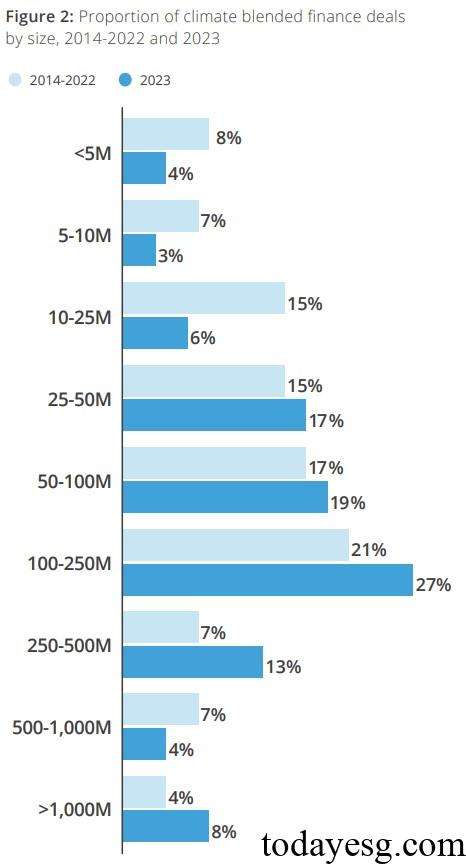
In addition to the continuous increase in total value, climate blended financing is also providing scalable solutions. The median size of global climate blended finance deals in 2023 reached $105 million, with $100 million deals accounting for 56% and $500 million deals accounting for 12%. In 2022, the proportion of financing with $100 million deals was only 23%, and the proportion of financing with $500 million deals was only 4%. In 2023, the Convergence database recorded a total of 6 climate blended finance deals with a scale exceeding $1 billion, which is equivalent to the total scale of this level in the past five years.
In climate blended finance deals, development financial institutions and multilateral development banks can boost the confidence of other investors. The Convergence finds that in climate financing deals exceeding $100 million, when there are development finance institutions and multilateral development banks present, $1 in concession capital can mobilize $2.1 in private sector financing. Without these institutions, this value drops to 0.8. In climate financing deals exceeding $500 million, when there are development finance institutions and multilateral development banks present, $1 in concession capital can mobilize $5.9 in private sector financing. Without these institutions, this value drops to $1.
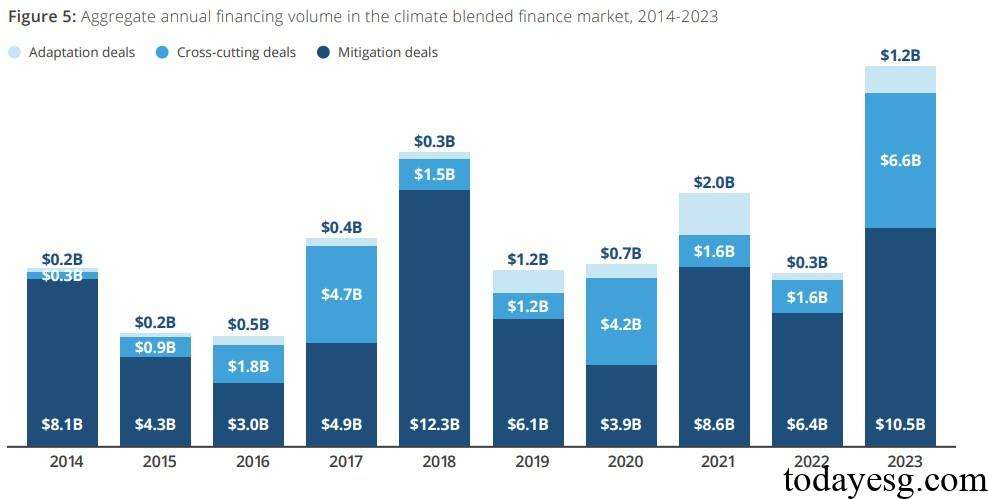
There are three main types of financing deals in the climate blended finance market, namely adaptation deals, mitigation deals, and cross-cutting deals. The global climate blended finance scale in 2023 is $18.3 billion, and adaptation deals, mitigation deals, and cross-cutting deals accounts for $1.2 billion, $10.5 billion, and $6.6 billion, respectively. Since 2014, mitigation deals have been at the core of the climate blended finance market, with a median deal size of $91.5 million, higher than adaptation deals ($39 million) and cross-cutting deals ($57 million). The leverage ratio of mitigation deals (3.6) is also higher than that of adaptive deals (2.12) and cross-cutting deals (2.8).
Reference:








