Guide on Climate-related Disclosure for Central Banks
The Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) releases the second edition of Guide on Climate-related Disclosure for Central Banks, aimed at helping global central banks prepare for climate information disclosure.
In December 2021, the NGFS released the first edition of Guide on Climate-related Disclosure for Central Banks, which provide initial templates for climate information disclosure for NGFS members. With the development of global climate disclosure standards, NGFS revises some important contents in the second edition of the guide to align with industry developments.
Related Post: Development of Global Climate Disclosure Policy
Introduction to Guide on Climate-related Disclosure for Central Banks
The NGFS believes that central banks should implement climate information disclosures consistent with international standards, which can improve pricing mechanisms for climate related risks and enable market participants to identify and utilize climate related opportunities. Climate information disclosure can also help central banks identify and assess climate related risks and consider the impact of climate when formulating regulatory policies.
Most central banks around the world are not subject to mandatory regulatory policies, and there are significant differences between central banks, enterprises and public institutions. The NGFS considers the internal functions of central banks in its information disclosure guidelines, such as formulating monetary policies, providing financial supervision, and holding investment portfolios. The guide will provide central banks with different ranges and depths of choices, including climate issues recommended for disclosure and climate issues encouraged for disclosure.
Contents of Guide on Climate-related Disclosure for Central Banks
To improve the consistency between Central bank’s climate information disclosure and international information disclosure standards, the NGFS adopts the guidelines of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures. It is recommended that Central bank carry out information disclosure through the following four pillars:
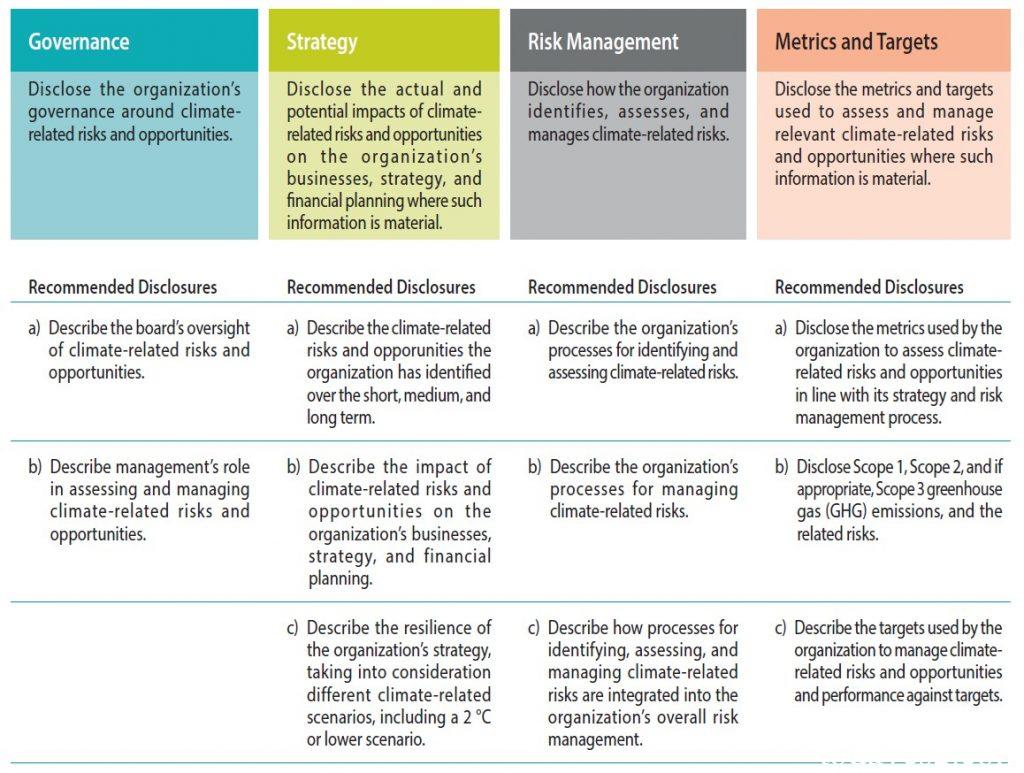
- Governance: Stakeholders such as governments, financial institutions, and the public are interested in learning about central bank actions in regulating climate risks, which can enhance public confidence in central bank management of climate change and achieving climate governance. Central bank should elaborate on its governance structure for addressing climate related risks and opportunities and clarify the role of central bank management in the design, implementation, and supervision of climate policies. Central bank can also disclose departments and committees specifically established to address climate related issues.
- Strategy: Central bank needs to disclose how it is affected by climate related risks and opportunities, and how it takes action to address these impacts. These disclosures include identifying climate factors that pose material risks and how these factors are identified and evaluated. Central bank also needs to disclose strategies for incorporating climate risks and opportunities into monetary policy, financial regulation, investment portfolios, as well as internal construction, external communication, and industry cooperation in response to climate change issues.
- Risk Management: Climate risk management information can help stakeholders understand how central banks identify, assess, and manage climate risks. Central bank needs to consider whether to classify climate risk as a separate risk category or treat it as an ancillary part of traditional risks such as market risk and credit risk. Central bank can also disclose how it limits climate related risks and whether it has sufficient financial resources to address these risks.
- Metrics and targets: Central bank needs to provide indicators for calculating or evaluating climate risks, as well as the calculation methods and specific results of these indicators. For example, the carbon emission intensity and total greenhouse gas emissions information of the investment portfolio held, as well as the Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3 carbon emission data generated in its business activities. Central bank plays an important role in financial market regulation, and can also disclose its management on climate risks in regulations.
The NGFS believes that the second edition of Guide on Climate-related Disclosure for Central Banks will help central banks better analyze and manage climate related risks and opportunities. In the future, the NGFS will consider incorporating natural related risks into Central bank’s information disclosure framework.
Reference:
NGFS Publishes the Second Edition of its Guide on Climate-related Disclosure for Central Banks








